መነሻ ገጽ » ጥቂት ስለ አገሪቱ ሥርዓት » የተባበሩት አረብ ኢሚሬትስ
Brief History of UAE
- History of UAE
- Hierarchical structure
- The Constitution of UAE
- Federal Government
- Emirates Government
- Election
History of the UAE
Ancient History: In ancient times, the Persian Gulf, where the modern-day UAE is situated, was relatively cut off from other people. With vast deserts and treacherous mountains cutting the gulf off from most other contact, countries of the Persian Gulf only really communicated between themselves. The countries found in the Persian Gulf included (modern-day) the UAE, Oman, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait, Iraq, Iran, and others. These countries were influenced by the power of several empires, including the Ottoman Empire, the Sassanid Persian Empire, and the Parthian Empire. These empires and countries were famed for their naval prowess, and piracy was common along the Gulf.
Colonization: In the 1500s, Portuguese naval forces attempted their first invasions of the Gulf. Battling with Ottoman forces, the Portuguese conquered many of the Gulf countries and were not expelled for around 100 years. The Persian Gulf supplied trade routes to North Africa, India, and China, and was a valuable port for long voyages from Europe. The main trade of the Gulf countries was pearls, and these made up a large part of the history of the UAE and surrounding countries.

To overthrow Portuguese rule, the help of the British Navy was enlisted by the Persian emperor of 1622. This opened the gulf for more trade, and for many years the region prospered. The East India Trading Company and Kuwait formed alliances to help the British capitalize on this trade route and the booming pearl trade, and all was well for many years: the UAE and the Persian Gulf were peaceful.
Modern history of the UAE: In more modern times, at the start of the 19th century, the Gulf was ruled by the Sheiks. Much like an emirate, this was a territory ruled by a Sheik. Piracy had started to creep back into the waters of the gulf, and so to secure their trade in the region the British signed treaties for naval truce with many Sheikdoms. In 1853 this necessitated the creation of the Trucial States, which was a group of Sheikdoms that formed under the protectorate of the British, in return for piratical immunity. The British had control of foreign policy in the Trucial States for several years, although it cost them lots of money, and towards the end of the 19th century, they stopped seeing much point in the arrangement.
In the early 1900s, things changed forever in the Persian Gulf. With the invention of artificial pearls, the region’s main trade was devalued and eventually ceased. Many people moved away from the cities hoping to find work elsewhere, and for a while, the UAE was deserted. However, after a few years of hardship, one discovery in Iraq changed everything: oil.
Upon discovering this hugely valuable commodity, people quickly emigrated to the UAE, and populations rose again. To defend their new resource, the Trucial States decided to become independent of the British and formed the United Arab Emirates. The British stopped their protectorate in 1968, then three years later, on 2nd December 1971, the UAE was formed. This originally included 6 emirates, with Ras Al Khaimah joining two months later, to make the 7 emirates we know today.
Is the UAE a country? The United Arab Emirates is a country located in the Persian Gulf and is made up of 7 emirates. An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, which means the UAE is governed by 7 emirs. These 7 emirs work together to form a governing body, from which a president is elected as the main figurehead for the UAE. This spokesperson is elected from Abu Dhabi, which is the largest and richest of the 7 emirates.
The emirates in the UAE: There are 7 emirates in the UAE, and contrary to popular belief, they are not all bustling desert cities. Abu Dhabi is the largest emirate, with Dubai being the second largest. These two emirates make up most of the wealth of the UAE and are the emirates people think of most frequently when the UAE is mentioned. The other emirates are smaller, and in many places are much more modest. Listed in order of size, the 7 emirates of the UAE are:
- Abu Dhabi
- Dubai
- Sharjah
- Ras Al Khaimah
- Fujairah
- Umm Al Quwain
- Ajman
It’s also worth noting that the capital city of each emirate has the same name as the emirate territory. The capital city of Abu Dhabi is Abu Dhabi, whilst this is also the name of the whole region. Abu Dhabi (capital) is 972 km2, whereas the region is 67,340 km2. This makes the capital only 1.4% of the entire Abu Dhabi regional area.
Hierarchical Structure of the UAE
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has a hierarchical structure of government and leadership that reflects its federal system and the individual governance of its seven emirates. Here’s an overview of this structure:
Federal Structure: The UAE is a federation of seven emirates, each of which retains a considerable degree of autonomy. The seven emirates are Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm Al-Quwain, Fujairah, and Ras Al Khaimah.
Federal Supreme Council (FSC): The highest authority in the UAE is the Federal Supreme Council. This council consists of the rulers of each of the seven emirates. They convene to make significant decisions on national issues, including the election of the President and Vice President of the UAE.
President and Vice President: The President and Vice President of the UAE are elected from among the members of the Federal Supreme Council. The President serves as the head of state, while the Vice President assists in carrying out the federal functions. The President is also the ruler of Abu Dhabi, the largest and wealthiest emirate.
Cabinet: The UAE Cabinet, also known as the Council of Ministers, is responsible for formulating and implementing federal policies and laws. It is composed of ministers, each of whom oversees specific government ministries and departments. The Prime Minister chairs the Cabinet.
Prime Minister: The Prime Minister is appointed by the President and is usually the ruler of Dubai. The Prime Minister presides over Cabinet meetings and assists in the day-to-day administration of federal affairs.
Federal National Council (FNC): The Federal National Council is a legislative body with advisory powers. Its members are partially appointed and partially elected by the citizens of each emirate. The FNC reviews and suggests changes to federal laws and policies but does not have the authority to enact legislation. It serves as a platform for public discourse and engagement in federal matters.
Emirate-Level Government: Each emirate has its government structure, headed by a ruler or emir. The ruler appoints an executive council or cabinet to manage the emirate’s affairs. These emirate-level governments have authority over a wide range of local issues, including infrastructure, education, healthcare, and social services.
Local Councils: Emirate-level governments may establish local councils or municipalities responsible for local governance, public services, and urban planning. These councils’ specific structure and responsibilities can vary from emirate to emirate.
Judiciary: The UAE has an independent judiciary system, with both federal and emirate-level courts. The federal judiciary is responsible for interpreting federal laws, while the emirate-level courts handle issues that fall within the jurisdiction of individual emirates. The Federal Supreme Court serves as the highest judicial authority in the country.
The hierarchical structure of the UAE’s government is designed to balance the authority of individual emirates with the need for unified federal governance. This structure has contributed to the country’s political stability and economic development while respecting the distinct identities and traditions of each emirate.
The UAE Constitution
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) does not have a single, comprehensive written constitution like many other nations. Instead, the UAE’s constitutional framework is based on a combination of sources, including historical agreements, federal laws, and Islamic law principles (Sharia). Here’s a brief overview of the key elements of the UAE’s constitutional framework.

Historical Agreements: The UAE’s constitutional framework is primarily based on historical agreements between the seven emirates. These agreements include the “Union Agreement” signed on December 2, 1971, which established the UAE as a unified nation. Another important document is the “Constitution of the United Arab Emirates” issued by the Federal National Council (FNC) in 1996, which outlines the basic principles and structure of the federal government.
Islamic Law (Sharia): The UAE’s legal system is influenced by Islamic law, or Sharia. Sharia principles are embedded in the legal and judicial systems of the country and play a significant role in shaping its laws and regulations, particularly in family and personal matters.
Federal System: The UAE’s constitution emphasizes the federal nature of the country, recognizing the individual authority and autonomy of each emirate. The emirates have the right to manage their local affairs and resources.
Role of the Federal Supreme Council: The Federal Supreme Council (FSC), composed of the rulers of the seven emirates, is the highest constitutional authority in the UAE. The FSC has the power to make important decisions related to the federal structure, including electing the President and Vice President of the UAE.
Principles of Governance: The constitution establishes key principles of governance, including the rule of law, democracy, the separation of powers, and respect for human rights.
Federal National Council (FNC): The FNC is a key component of the UAE’s constitutional framework. While it is an advisory body without legislative powers, it plays a role in discussing and proposing changes to federal laws and policies.
Presidential Authority: The President of the UAE, elected by the FSC, holds executive authority at the federal level and represents the UAE internationally. The Prime Minister, usually the ruler of Dubai, assists the President in the administration of federal affairs.
Judiciary: The UAE has a well-established judiciary with federal and emirate-level courts. The Federal Supreme Court serves as the highest legal authority in the country, responsible for interpreting federal laws and resolving disputes between emirates.
Fundamental Rights and Freedoms: The UAE’s constitution recognizes fundamental rights and freedoms, including the right to equality, education, healthcare, and a fair trial. It also emphasizes the importance of preserving cultural heritage and the Arabic language.
It’s important to note that the UAE’s constitutional framework is a mix of written and unwritten elements, with flexibility that allows for adaptations and evolution over time. Federal laws, decrees, and regulations fill in many details and provisions, effectively shaping the legal and political landscape of the country.
The Federal Government of the UAE
The Federation aims to maintain its independence and sovereignty, safeguard its security and stability, defend its existence or the existence of its member emirates from any act of aggression, and protect the rights and responsibilities of the people of the Federation. It aims to work in close cooperation with each of the emirates for their common benefit in realizing these objectives and promoting their prosperity and progress in all fields to provide a better life for all citizens, ensuring mutual respect by each emirate for the independence and sovereignty of the other emirates in matters related to their internal affairs within the framework of the Constitution.
The Federal Authorities in the UAE: The UAE Federal Authorities include the Federal Supreme Council, the President and Vice President, The Cabinet, the Federal National Council, and the Federal Judicial Authority.
Each emirate of the UAE shall handle all authorities not assigned by the Constitution to the Federation. Moreover, each emirate shall contribute to building and protecting the Constitution as well as benefiting from its services. All member emirates of the Federation will strive to coordinate their legislatures in all areas to achieve standardization.
The federal government of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has three main branches, like many other democratic nations. These branches are:
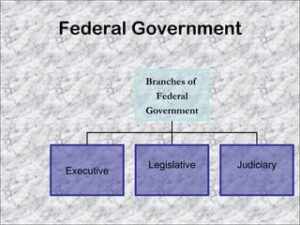
The Executive Branch: The executive branch of the federal government of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is headed by the President and Vice President, both of whom are elected by the Federal Supreme Council (FSC). The President serves as the head of state and represents the UAE on the international stage, while the Vice President assists in executing federal functions. The executive branch also encompasses the Cabinet, and the Council of Ministers, responsible for developing and implementing federal policies and laws. The Prime Minister, typically the ruler of Dubai, presides over Cabinet meetings and plays a crucial role in the administration of federal affairs. The executive branch is responsible for the day-to-day governance of the UAE, including the implementation of laws and policies at the federal level.

The legislative branch: The legislative branch of the federal government in the United Arab Emirates is embodied by the Federal National Council (FNC). The FNC serves as a crucial component of the UAE’s political landscape, acting as a consultative and advisory body. Its members are drawn from each of the seven emirates, with some being appointed by the respective emirate rulers and others being elected by citizens. While the FNC does not possess legislative powers, it plays a significant role in the decision-making process by reviewing and proposing changes to federal laws and policies. As a platform for public discourse and engagement, the FNC provides a voice for the citizens, contributing to the development of federal laws and ensuring that the government remains responsive to the needs and concerns of the people.
The judicial branch: The judicial branch of the federal government of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) comprises federal and emirate-level courts. At the federal level, the Federal Supreme Court serves as the highest judicial authority in the country. It is responsible for interpreting federal laws, resolving disputes between emirates, and ensuring uniformity in the application of legal principles across the nation. The emirate-level courts handle issues that fall within the jurisdiction of individual emirates, including local disputes and civil matters. This dual-tiered judicial system aims to provide citizens and residents with access to justice while maintaining a harmonious balance between federal and emirate-level governance within the UAE’s legal framework.

These three branches work together to govern the UAE, with the executive branch responsible for implementing policies, the legislative branch providing advice and discussion on legislation, and the judicial branch ensuring that the rule of law is upheld. The UAE’s political system is designed to maintain a balance between federal and emirate-level governance.
Emirates Government
The government structure in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is based on a federal system that combines elements of a federal government with strong centralized authority. While I’ve previously discussed the broader aspects of the UAE’s government, here are the key aspects of the Emirates’ local government:
Rulers of the Emirates: The UAE comprises seven emirates, each headed by a hereditary ruler. These rulers are the ultimate authority within their respective emirates and play a central role in shaping policies, governance, and development within their territories.
Executive Councils: Each emirate has its own Executive Council, which serves as the highest executive authority within the emirate. The Executive Council is typically chaired by the ruler of the emirate and includes other key officials and advisors. It is responsible for managing local government affairs, developing policies, and overseeing the implementation of various initiatives.
Local Government Departments: Local government departments within each emirate handle a wide range of functions, such as education, healthcare, public infrastructure, urban planning, transportation, and public services. These departments are tasked with ensuring that the daily needs and services of the emirate’s residents are met.
Municipalities: Local municipalities operate within each emirate to manage urban planning, public spaces, and the delivery of municipal services. They are responsible for maintaining infrastructure, parks, and other local facilities. Municipal councils, often consisting of elected and appointed members, contribute to local governance and decision-making.
Economic Development: Each emirate has its approach to economic development and diversification. Some emirates, like Abu Dhabi and Dubai, have established major economic free zones and diversified their economies through sectors like finance, tourism, and industry. The emirates collaborated on some aspects of economic policy at the federal level to ensure a coordinated approach.
Cultural and Social Development: The emirates also invest in cultural and social development. They support initiatives related to education, healthcare, arts, culture, and heritage preservation. Additionally, they often have cultural and sports authorities that organize events, exhibitions, and activities to promote their cultural identity and heritage.
Local Laws and Regulations: Each emirate can enact its local laws and regulations within the framework of the UAE’s federal laws. This allows emirates to address issues specific to their region, although federal laws generally take precedence in areas such as criminal law and foreign policy.
Security and Law Enforcement: Local law enforcement agencies are responsible for maintaining law and order within each emirate. These agencies handle local security matters and collaborate with federal law enforcement agencies on broader security concerns.
Local Judicial System: While there is a federal judiciary in the UAE, each emirate also has its local court system responsible for civil, criminal, and family matters. The local judicial system works in conjunction with the federal legal framework.
Participation and Consultation: Emirati citizens often have opportunities to participate in local governance through various channels, such as advisory councils and public consultations. The level of citizen participation can vary from one emirate to another.
The key aspect of the Emirates’ government in the UAE is that each emirate has a considerable degree of autonomy in managing its affairs, including economic development, social services, and local governance. This system allows the emirates to tailor policies to their unique needs and priorities, while the federal government handles matters of national interest and foreign policy.
Federal Elections
Federal elections in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) are a significant aspect of the country’s political landscape, allowing Emirati citizens to participate in selecting representatives for the Federal National Council (FNC). The FNC is the UAE’s legislative body with advisory and limited legislative powers at the federal level. Here are the key points about federal elections in the UAE:

Limited Electoral System: The UAE has a limited electoral system, where eligible voters are Emirati citizens. Expatriates, who make up a significant portion of the UAE’s population, do not have the right to vote in federal elections. Eligible voters must meet certain criteria, including being at least 25 years old and having a family book (Khulasat Al Qaid) that certifies their Emirati citizenship.
Electoral College: The electoral system in the UAE uses an electoral college, with half of the members of the Federal National Council (FNC) being elected by the citizens, and the other half being appointed by the rulers of the seven emirates. The total number of FNC members can vary depending on decisions by the rulers, but it has typically been around 40 members.
Emirate Representation: The number of FNC members elected by each emirate is determined by its population. As a result, the more populous emirates, such as Dubai and Abu Dhabi, have more elected members in the FNC. Each emirate has its own electoral body to oversee the election process.
Electoral Committees: Electoral committees are established in each emirate to facilitate the election process. These committees manage voter registration, candidate registration, and the overall organization of the elections. They also ensure that the elections are conducted in a free and fair manner.
Candidates: To run for the FNC, candidates must meet specific eligibility criteria, including being at least 25 years old, holding Emirati citizenship, and having a good reputation. Candidates must also present a specified number of signatures from registered voters in their respective emirates as a show of support.
Campaigning: Candidates are allowed to campaign to inform voters about their platforms and policies. Campaigning typically includes rallies, meetings, and the use of traditional and social media.
Voting Process: UAE citizens who meet the eligibility criteria and have registered to vote can participate in the elections. Voting is done in person at designated polling stations, which are set up in various locations across the Emirates. The voting process is secure and transparent.
Election Results: The winners of the elections become members of the Federal National Council. They serve four-year terms. The FNC members elected by the citizens and the appointed members work together to represent the interests of the UAE’s population and provide advice and recommendations on various issues to the government.
Role of the FNC: The FNC has both advisory and legislative functions. While its decisions are not binding, it plays a crucial role in discussing and proposing federal laws and regulations. It also provides input on national policies, budgets, and other important matters.
Political Engagement: Federal elections in the UAE are seen as an opportunity for Emirati citizens to engage in the political process and have a voice in the country’s governance. The UAE government has taken steps to promote civic participation and encourage greater political engagement among its citizens.
It’s important to note that the political landscape in the UAE is unique, and the country has a political system that combines elements of traditional and modern governance. Federal elections are part of a broader political framework in which the leadership values stability, continuity, and consensus in decision-making.
Emirates Elections
Elections in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) are limited in scope and primarily take place at the federal and local levels, with varying degrees of political participation. Here are the key points related to elections in the UAE:
Federal National Council (FNC) Elections:
The FNC is the federal legislative body in the UAE, and half of its members are elected. The FNC is responsible for reviewing and proposing federal laws and discussing national issues. FNC elections are held every five years. In the elections, a limited number of Emirati citizens are eligible to vote or run for office. Eligible voters are appointed by the rulers of each emirate to represent the electorate. The FNC has 40 members, with half of them elected. In the 2019 elections, 20 members were elected, and 20 members were appointed.
Electoral Process: FNC elections use a specific electoral college system where eligible voters in each emirate choose half of the FNC members. The electoral process involves a select group of Emirati citizens, including tribal leaders, intellectuals, and community figures, who are tasked with nominating candidates and voting for the FNC members.
Limited Eligibility: Eligibility to participate in FNC elections is restricted. Citizens who meet certain criteria, such as age, education, and community standing, may be selected by the emirate’s rulers to participate in the electoral process.
Nomination and Campaigning: Emiratis interested in running for the FNC must seek nomination from the electoral college members. Campaigning for FNC elections is a controlled process, and candidates are expected to adhere to strict guidelines and avoid controversial or divisive issues.
Representation: The FNC represents the interests of the UAE’s citizens and addresses their concerns, but its powers are limited. It can review and propose federal laws but doesn’t have legislative authority. The appointed members of the FNC, who are not elected, serve to complement the council’s work.
Local Council Elections: Some emirates, such as Dubai and Abu Dhabi, have introduced local council elections at the emirate level. These elections allow eligible Emirati citizens to participate in selecting local representatives who focus on municipal and community matters.
It’s important to note that while elections in the UAE represent a step toward political participation, the system is characterized by limited suffrage and significant control by the ruling families and authorities. The emphasis is on maintaining stability, national unity, and a measured transition toward more inclusive political processes.
Political Parties
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) does not have traditional political parties as seen in many other countries. Instead, the UAE operates under a system where political participation and power are primarily held by the ruling families of each of the seven emirates. The political landscape is characterized by a lack of formal political parties, and the focus is on consensus-building and maintaining stability. However, there are some noteworthy aspects related to political participation and entities that play a role in shaping policy and governance in the UAE:
Federal National Council (FNC): The FNC is the closest entity to a legislative body in the UAE, and it is responsible for discussing national issues and reviewing and proposing federal laws. While not a political party in the traditional sense, the FNC includes members who represent different emirates and serve as representatives of their communities. Half of the FNC’s members are elected, while the other half are appointed by the rulers of the emirates.
Ruling Families: The ruling families of the seven emirates, particularly the rulers, play a central role in shaping policy and governance. They wield significant influence in decision-making at both the emirate and federal levels. The rulers of the emirates are responsible for appointing members to the electoral college for FNC elections and hold considerable authority over key appointments and decisions.
Elite Advisory Bodies: The UAE has established elite advisory bodies that contribute to policy discussions and provide counsel to the government. These include the Abu Dhabi Executive Council, Dubai Executive Council, and other similar entities in different emirates. These advisory councils consist of prominent individuals, experts, and community figures who advise the rulers on various matters.
Civil Society Organizations: While not political parties, there are civil society organizations and non-governmental groups that focus on specific issues and work to influence policy decisions in the UAE. These organizations often have specific goals related to areas such as culture, education, social development, and healthcare. They work closely with government bodies to achieve their objectives.
Women’s Representation: The UAE has made efforts to promote women’s participation in political and public life, including the Federal National Council. Women have achieved significant representation in the FNC, and the government has supported initiatives to empower women in various fields.
It is important to understand that the political landscape in the UAE differs significantly from multi-party democratic systems. The UAE’s political structure is focused on maintaining stability, national unity, and consensus, and political power is largely concentrated in the hands of the ruling families and government authorities. While there are avenues for participation and input from Emirati citizens and advisory bodies, formal political parties do not exist as independent entities with the power to compete in elections and shape the direction of the government.
Immigration System of UAE
- Immigration Overview
- Types of Immigration
- Asylum
- The Asylum in UAE
UAE Immigration Overview
The immigration system in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is well-structured and regulated, reflecting the country’s role as a hub for international business, tourism, and expatriate employment. It offers various types of visas and residency options, including tourist visas for short-term visits, employment visas for those joining the workforce, family visas for residents’ relatives, student visas for educational pursuits, and investor visas for individuals making significant financial commitments. The UAE also introduced long-term residency (Golden Visa) options to attract investors, skilled professionals, and outstanding students. The specific documents and requirements vary depending on the type of visa or residency sought. While the UAE is open to welcoming expatriates from around the world, its immigration system is characterized by certain regulations and requirements, ensuring that those entering the country meet the established criteria for their intended stay. It’s advisable for individuals considering relocation to the UAE to consult with the relevant authorities or sponsors to navigate the application process and remain compliant with the latest immigration regulations.
Legal Immigration: Legal immigration to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) involves obtaining the appropriate visa or residency status for your intended purpose, such as employment, family reunification, study, or investment. The process typically requires a valid passport, the completion of visa application forms, relevant documentation (e.g., job offer letters, sponsorship letters, educational certificates), and compliance with medical and security checks.
Visa types: The UAE has various types of visas, including tourist visas, employment visas, family visas, student visas, and investor visas. In some cases, long-term residency options are available. It’s essential to adhere to UAE immigration regulations, which can change periodically, and to work with the relevant authorities or sponsors to ensure a smooth and legal immigration process.
Golden Visa: The Golden Visa program in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a prestigious and long-term residency initiative that offers eligible investors, entrepreneurs, skilled professionals, and outstanding students the opportunity to secure extended residency for 5 or 10 years. It is designed to attract individuals who make significant financial investments, contribute to the UAE’s economy, or excel in their fields of expertise. The program varies slightly between emirates but generally requires applicants to meet specific investment or qualification criteria, such as property investments, business ventures, academic achievements, or outstanding skills.
Naturalization: Naturalization in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) refers to the process by which foreign individuals can become Emirati citizens. It is a selective and highly regulated process, typically requiring exceptional contributions to the UAE, including significant investments, outstanding achievements, or exceptional services. The criteria for naturalization are not publicly disclosed and can vary, but individuals who are granted Emirati citizenship gain access to the country’s extensive benefits, including social services, the right to own property, and participation in the country’s economy and society. Naturalization is not a common pathway to UAE citizenship, and the government exercises discretion in granting it.
Application Process: The application process for immigration to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) involves several steps. First, you must secure a sponsor, which can be an employer, family member, or educational institution, depending on your visa type. The sponsor will initiate the visa application. After submitting your application and documents, you’ll typically need to attend biometric data collection. Once your visa is approved, you’ll receive your entry permit. On arrival in the UAE, you’ll need to complete the residence visa process, including medical tests and fingerprinting. Keep in mind that visa requirements can change, so it’s essential to verify the latest regulations with the UAE’s General Directorate of Residency and Foreigners Affairs or the relevant UAE embassy or consulate.
Importance of legal assistance: Legal assistance is of paramount importance for immigration to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) due to the country’s strict and evolving immigration regulations. A qualified immigration attorney can help applicants navigate the complex visa and residency processes, ensuring all required documents are in order, and that applicants meet eligibility criteria. Legal experts can also guide the latest legal changes and visa options, helping individuals make informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls. Given the UAE’s commitment to maintaining security and controlling expatriate inflow, legal assistance is instrumental in ensuring a smooth and successful immigration experience, whether for employment, business, or family reunification in the UAE.
Rights and Responsibilities: Immigrants in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) enjoy certain rights and are expected to fulfill specific responsibilities. Immigrants have the right to work, access public services, and practice their religion. They are entitled to legal protections, such as fair treatment and access to the judicial system. However, immigrants must respect local laws, customs, and culture. They are responsible for abiding by the UAE’s strict legal and moral standards, including adhering to labor regulations and respecting Islamic traditions.
Resources and Supports: The United Arab Emirates (UAE) provides immigrants with a range of resources and support to help them integrate and thrive in the country. These include access to quality healthcare and education, as well as legal protections for workers. The UAE also offers cultural and religious tolerance, with various places of worship and diverse expatriate communities. Additionally, the government has introduced policies to enhance long-term residency options for investors, entrepreneurs, and skilled professionals.
Types of UAE Immigration
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has various immigration types and visa categories to regulate the entry and residence of foreigners in the country. These immigration types are subject to change and have specific eligibility requirements and conditions. Here are some of the key UAE immigration types:
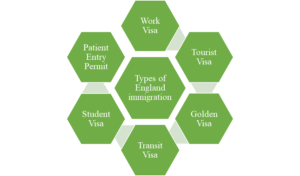
UAE Work Visa: A UAE Work visa is usually used for expats taking up a job in the UAE which is valid for 2 years for LLCs and 3 years for free zone companies. A residence visa should be applied by the employer (sponsor), medical is mandatory to get this visa. In 2019, the UAE implemented a new system for long-term residence visas. The new system enables foreigners to live, work, and study in the UAE without the need for a national sponsor and with 100 percent ownership of their business on the UAE’s mainland. These residence visas will be issued for 5 or 10 years and will be renewed automatically.
Tourist Visa: A UAE Tourist visa is for those who are not eligible for a visa on arrival or a visa-free entry to the United Arab Emirates. Tourist visas can be obtained for eligible individual tourists from around the world. Females below the age of 18 are not eligible to apply for this type of visa unless they are traveling with their parents. According to a Cabinet resolution passed in July 2018, children under the age of 18 years who are accompanying adults can get a free visa for their visit from 15 July to 15 September each year. Depending on your plan, tourist visas to the UAE can be issued for 30 days or 90 days duration, single entry or multiple entries.
Golden Visa: The UAE’s Golden Visa is a long-term residence visa that enables foreign talents to live, work, or study in the UAE while enjoying exclusive benefits which include an entry visa for six months with multiple entries to proceed with residence issuance, a long-term, renewable residence visa valid for 5 or 10 years, the privilege of not needing a sponsor, the ability to stay outside the UAE for more than the usual period of six months to keep their residence visa valid, the ability to sponsor their family members, including spouses and children regardless of their ages, the ability to sponsor an unlimited number of domestic helpers, and the permit for family members to stay in the UAE until the end of their permit duration if the primary holder of the Golden visa passes away.
Transit Visa: There are two types of transit visas: one for 48 hours which is free of charge and another for 96 hours for AED 50 only. Transit visas are sponsored only by UAE-based airlines and must be processed and approved before entering the UAE. Both types of transit visas are not extendable. To get a UAE transit visa, you must have a passport or travel document with a minimum validity of three months, A photo of yourself against a white background, and, an onward ticket booking to a 3rd destination, other than the one you are coming from.
Student Visa: A UAE student’s visa is a 1-year renewable visa for a university or a college student studying in the UAE. It is issued to expatriate students who are residing in UAE under the sponsorship of their parents or relatives, or to foreign international students who come from abroad to join one of the higher educational institutes across UAE. On 24 November 2018, the UAE government approved a decision to grant a 5-year visa to outstanding students. School students must graduate with a grade of at least 95 percent from secondary schools whether public or private. University students must graduate with a distinctive GPA of at least 3.75 from universities within and outside the country.
Patient Entry Permit: Through a patient entry permit foreign patients can enter the UAE for treatment under the sponsorship of medical establishments and government and private hospitals. The sponsor (medical establishment) takes the responsibility of processing entry permits for treatment upon the patient’s request. The sponsor must be a hospital licensed and registered in the UAE. The documents needed to process the entry permit include the Patient’s passport copy, a letter from a registered hospital explaining the reasons for the visit, the Patient’s health insurance, and financial security.
It’s important to note that immigration regulations and visa categories may have changed since my last knowledge update. The specific requirements, fees, and processes can vary between emirates within the UAE, so it’s essential to check with the relevant UAE authorities or the official government website for the most up-to-date information and requirements for each immigration type.
Asylum
Asylum is a legal status granted by a country to foreign nationals who are unable or unwilling to return to their home country due to well-founded fears of persecution based on their race, religion, nationality, political beliefs, or membership in a particular social group. The primary purpose of asylum is to provide protection to individuals who face persecution in their home country and to ensure their safety. Asylum seekers are typically granted certain legal rights and protections while their asylum claims are being assessed.
Here are some key points to understand about asylum in general:
Eligibility: To be eligible for asylum, individuals must demonstrate that they have a well-founded fear of persecution on the grounds of one of the protected categories mentioned earlier. They must prove that they cannot obtain protection in their home country.
Asylum Process: The asylum process typically involves an application or petition, interviews with immigration officials, and the presentation of evidence to support the asylum claim. This process can vary from country to country.
Refugee Status: If an individual’s asylum claim is approved, they are typically granted refugee status. This status provides them with legal rights and protections, including the right to work and live in the host country.
Rights and Benefits: Asylum seekers and refugees are entitled to certain rights and benefits, which may include access to healthcare, education, and social services. They are also protected from deportation to their home country.
Temporary vs. Permanent Asylum: Some countries grant temporary asylum, while others offer permanent asylum or a path to citizenship. The specific terms and conditions vary depending on the country’s laws and policies.
Asylum in the UAE
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) does not have a formalized asylum system or a specific legal framework for granting asylum or refugee status, which is why it does not grant asylum in the traditional sense as many Western nations do. Instead, the UAE approaches cases of individuals seeking protection on a case-by-case basis, often in response to humanitarian or geopolitical crises. While the country has a history of providing humanitarian assistance and temporary shelter to those affected by conflicts or persecution, its approach is not characterized by a formal asylum application process, refugee status recognition, or permanent asylum status. As a result, those seeking asylum in the UAE may find that their cases are handled differently compared to countries with established asylum systems, which can make the process less predictable and may not provide the same legal rights and protections associated with refugee status in other nations. The UAE’s approach to asylum is shaped by its commitment to humanitarian aid and support, but it may not align with the conventional international asylum framework as defined by the 1951 Refugee Convention. It’s essential for individuals seeking asylum in the UAE to consult with legal experts or relevant authorities in the country for the most accurate and up-to-date guidance on their specific situations.
Financial System of UAE
- Overview of the UAE Financial System
- Banking System
- Islami Finance
- Stock Market
- Financial Free Zones
- Real estate and investments
- Foreign Investment
- Sovereign wealth funds
- Regulatory Framework
UAE Financial System Overview
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) boasts a dynamic and sophisticated financial system that underpins its rapidly growing economy. At the core of this system is a well-developed banking sector, comprising both local and international banks, all regulated by the vigilant Central Bank of the UAE. These institutions offer a wide range of services, from retail banking to corporate finance, contributing significantly to economic development.
One distinguishing feature of the UAE’s financial landscape is its leadership in Islamic finance. The country hosts numerous Islamic banks and financial institutions that provide Sharia-compliant products, attracting investors seeking ethical and interest-free financial solutions. This sector’s robust growth has solidified the UAE’s reputation as a global hub for Islamic finance.
In terms of capital markets, the UAE has two primary stock exchanges: the Dubai Financial Market (DFM) and the Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange (ADX). These exchanges serve as critical platforms for businesses to raise capital and investors to diversify their portfolios. Additionally, the country offers financial free zones, like the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and the Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM), which provide an enticing environment for financial institutions and fintech companies through special regulations and incentives.
The real estate market plays a pivotal role in the UAE’s financial system, attracting local and international investors to its burgeoning property sector. Cities like Dubai, in particular, have seen a boom in real estate development, contributing to economic growth and diversification.
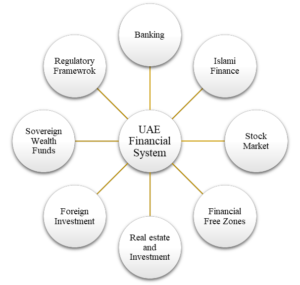
The UAE has also taken substantial steps to attract foreign investment, with liberalized regulations and double taxation avoidance agreements in place. This approach has made the country a favored destination for international investors looking for opportunities in a stable and business-friendly environment.
Sovereign wealth funds, including the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA) and the Investment Corporation of Dubai (ICD), are instrumental in managing the country’s vast wealth. These funds invest in a wide array of sectors worldwide, further diversifying the UAE’s financial portfolio.
The UAE Dirham (AED), pegged to the United States Dollar (USD), provides currency stability for international trade and investments, ensuring predictability in financial transactions. The regulatory framework in the UAE is robust, with the Central Bank and regulatory authorities like the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) overseeing the various aspects of the financial sector, ensuring the system’s integrity and stability.
In summary, the UAE’s financial system is renowned for its openness to foreign investment, innovation, and its role as a regional and global financial hub. This system has been a key driver of the country’s economic growth and diversification efforts, supporting its ambitions to become a dynamic and globally competitive economy.
Banking: The banking system in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a pivotal component of its financial sector, offering a wide range of services and contributing significantly to the country’s economic growth. It consists of various types of banks and financial institutions, each serving distinct functions within the financial landscape.
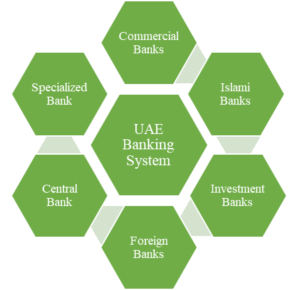
Commercial Banks: Commercial banks play a central and multifaceted role in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) financial system. These institutions are the backbone of the UAE’s banking sector, offering a wide range of financial services to individuals, businesses, and the broader economy. Commercial banks provide essential services such as savings and current accounts, loans, credit cards, and wealth management solutions, serving the daily financial needs of individuals. They also play a pivotal role in corporate banking, providing businesses with financing, and cash management services, and facilitating trade and international transactions. Notable commercial banks in the UAE include Emirates NBD, First Abu Dhabi Bank (FAB), and Dubai Islamic Bank.
Islamic Banks: Islamic banks play a significant role in the UAE’s financial system, adding a unique dimension to the country’s diverse banking landscape. These banks strictly adhere to Sharia principles, offering financial products and services that are compliant with Islamic law. They facilitate ethical and interest-free transactions, attracting a segment of customers seeking such alternatives. Islamic banks in the UAE provide a wide array of services, including Islamic financing, savings accounts, wealth management, and insurance. Their presence not only caters to the local population’s religious and ethical preferences but also contributes to the country’s leadership in Islamic finance, attracting international investors and positioning the UAE as a global hub for Sharia-compliant financial services. Moreover, their growth has helped diversify the financial sector, enhancing the overall resilience and competitiveness of the UAE’s financial system. Examples include Emirates Islamic Bank, Abu Dhabi Islamic Bank (ADIB), and Dubai Islamic Bank.
Investment Banks: Investment banks play a crucial role in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) financial system by facilitating a wide range of capital market activities and corporate finance functions. They are instrumental in supporting businesses and governments in raising capital through activities like underwriting securities, initial public offerings (IPOs), and bond issuances. Investment banks also provide advisory services, helping clients with mergers and acquisitions (M&A), corporate restructuring, and financial strategies. In a rapidly evolving financial landscape, they contribute to the development of innovative financial products and services. These institutions are pivotal in connecting investors with opportunities in the UAE’s dynamic and growing economy, making the country a vibrant hub for capital market activities and financial services.
Foreign Banks: Foreign banks play a significant and beneficial role in the UAE’s financial system. They bring global expertise, capital, and a wide array of financial services to the country, enhancing the depth and diversity of the financial sector. These banks facilitate international trade, connect UAE businesses to the global market, and offer a variety of specialized financial products and services. Their presence fosters competition, which can result in better financial products, services, and interest rates for consumers and businesses. Additionally, foreign banks attract foreign investments and contribute to the UAE’s status as a global financial hub, further solidifying the country’s position as an international business and finance destination.
Central Bank: The Central Bank of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) plays a pivotal role in the country’s financial system. As the primary monetary authority, its responsibilities encompass regulating and supervising all banks and financial institutions operating within the UAE. The Central Bank formulates and implements monetary policy, managing interest rates and money supply to maintain price stability and economic growth. It also oversees the stability of the UAE Dirham (AED) and its peg to the United States Dollar (USD).
Specialized Banks: Specialized banks in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) play a targeted and crucial role within the country’s financial system. These banks are designed to address specific financial needs or promote certain economic sectors. For instance, they may focus on industrial development, agricultural financing, or housing loans. By catering to niche segments of the market, specialized banks help support the UAE’s economic diversification efforts and targeted development initiatives. They provide tailored financial services, often with a deep understanding of the unique requirements of their designated sectors. These institutions contribute to economic growth by channeling funds and expertise to sectors that are strategically important for the UAE’s long-term economic development, further enhancing the overall stability and sustainability of the country’s financial system.
The UAE’s banking system is characterized by its modernity, efficiency, and global connectivity. It has a strong regulatory framework in place, overseen by the Central Bank, to maintain the stability and integrity of the financial system. This well-diversified and regulated banking sector supports the country’s economic growth, attracting both local and international investors and contributing to the UAE’s position as a global financial hub.
Islami Finance
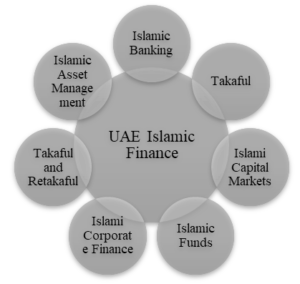
Islamic finance plays a significant role in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), where it has experienced substantial growth and innovation. This sector adheres to Islamic principles, primarily avoiding interest (usury) and promoting risk-sharing and ethical investment. Here’s a detailed but brief overview of Islamic finance in the UAE and its key types:
Islamic Banking: Islamic banks in the UAE offer financial services in compliance with Sharia principles. They operate without charging or paying interest, adhering to Islamic prohibitions on usury (riba). Instead, they engage in profit-and-loss sharing, trade-based financing, and asset-backed lending. Prominent Islamic banks in the UAE include Dubai Islamic Bank, Abu Dhabi Islamic Bank, and Sharjah Islamic Bank.
Takaful (Islamic Insurance): Takaful is an Islamic alternative to conventional insurance. In the UAE, Takaful companies provide insurance products that adhere to Sharia principles. Participants contribute to a common pool, and the funds are used to cover losses and liabilities. Companies like Takaful Emarat and Salama Islamic Insurance offer Takaful services in the UAE.
Islamic Capital Markets: The UAE hosts Sharia-compliant stock exchanges and investment instruments, such as Sukuk (Islamic bonds) and Sharia-compliant equities. The Dubai Financial Market (DFM) and Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange (ADX) facilitate the trading of these instruments. Sukuk are interest-free bonds that grant investors a share in the profits generated by the underlying assets.
Islamic Funds: In the UAE, various financial institutions offer Islamic investment funds, including mutual funds and real estate investment trusts (REITs), which comply with Islamic finance principles. These funds invest in assets that align with Sharia requirements, making them appealing to investors seeking ethical and Halal investment opportunities.
Islamic Corporate Finance: Islamic finance is increasingly used for corporate and project finance in the UAE. Businesses can obtain funding through Sharia-compliant contracts such as Mudarabah (profit-sharing), Murabaha (cost-plus financing), and Ijarah (leasing) to support their operations and expansion.
Takaful and Retakaful: These are reinsurance products adhering to Islamic principles. They provide insurance companies with risk management solutions that are consistent with Sharia law. Takaful companies in the UAE engage in re-takaful to spread their risk exposure.
Islamic Asset Management: Islamic asset management firms in the UAE offer investment and wealth management services that ensure portfolios are structured according to Sharia guidelines. These firms cater to individual and institutional investors seeking to invest in line with their faith.
In summary, the UAE’s Islamic finance sector has witnessed considerable growth and diversification, offering a wide range of financial products and services that adhere to Islamic principles. This has attracted not only the country’s Muslim population but also international investors seeking ethical and Sharia-compliant financial opportunities. Islamic finance types in the UAE encompass banking, insurance, capital markets, investment funds, corporate finance, and asset management, contributing to the country’s position as a global Islamic finance hub.
Stock Market
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has two primary stock exchanges: the Dubai Financial Market (DFM) and the Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange (ADX), each serving as a significant component of the country’s financial system.
Dubai Financial Market (DFM): The Dubai financial market is Situated in Dubai, the DFM is one of the UAE’s major stock exchanges. The DFM hosts a diverse range of listed companies, including local and international firms from various sectors such as real estate, finance, and telecommunications. The DFM operates under the supervision of the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA), the UAE’s primary regulatory authority for financial markets. The DFM attracts a broad investor base, including both institutional and retail investors. The DFM General Index is the main benchmark index, tracking the performance of listed companies on the DFM.

Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange (ADX): The Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange is located in Abu Dhabi, and the ADX is another key stock exchange in the UAE. The ADX also lists a diverse range of local and international companies, with a focus on sectors such as energy, banking, and industrial entities. The ADX is regulated by the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA), ensuring transparency and compliance with regulatory standards. Like the DFM, ADX caters to a wide spectrum of investors, including institutions and individual investors. The ADX General Index is the primary benchmark index for tracking the performance of companies listed on the ADX.

Both the DFM and ADX play crucial roles in facilitating capital raising for businesses and providing investment opportunities for both domestic and international investors. They contribute to the overall development and diversification of the UAE’s financial markets, making the country an attractive destination for investment in the Gulf region.
Financial free zones
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is home to several financial-free zones, which are designated areas with distinct regulations and incentives to attract businesses, particularly those in the financial and business sectors. These free zones offer an array of benefits to companies looking to establish a presence in the UAE. Here’s a detailed but concise overview of the major financial free zones in the UAE:

Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC): DIFC is a financial-free zone located in the heart of Dubai. DIFC is a well-established and highly reputable financial hub. It’s known for its modern infrastructure and a comprehensive legal framework based on English common law. It hosts a wide range of financial institutions, including banks, asset management firms, insurance companies, and fintech startups. DIFC offers 100% foreign ownership, zero tax on corporate income and profits, and no restrictions on capital repatriation.
Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM): ADGM is located in the capital city, Abu Dhabi. ADGM is another prominent financial free zone in the UAE. It’s known for its robust regulatory framework and flexible business setup options. ADGM hosts a diverse range of financial and professional services companies, including banks, insurance firms, and wealth management entities. It offers benefits such as full foreign ownership, zero taxes for a specified period, and a common law jurisdiction with English as the working language.
Dubai International Academic City (DIAC): DIAC is a free zone focused on the education sector. DIAC is designed to promote education and research. It’s home to a multitude of universities, colleges, and academic institutions. Businesses operating in DIAC enjoy benefits like 100% foreign ownership, full repatriation of profits, and access to a skilled talent pool in the education sector.
Dubai Media City (DMC) and Dubai Internet City (DIC): DMC and DIC are media and technology-focused free zones. These free zones cater to media, information technology, and communications companies. DMC is a hub for media-related businesses, while DIC is known for technology and digital companies. They offer business-friendly regulations, 100% foreign ownership, and tax exemptions.
RAK International Corporate Centre (RAK ICC): RAK ICC is an offshore free zone located in Ras Al Khaimah. RAK ICC is an offshore jurisdiction that caters to international businesses looking to establish a presence in the UAE. It provides offshore company registration, allowing companies to conduct activities outside the UAE. It offers privacy, asset protection, and tax benefits.
These financial free zones in the UAE serve as magnets for foreign investment, fostering economic growth and diversification. They offer a range of structures to accommodate various business needs, whether you’re a multinational corporation, a startup, or an educational institution, making the UAE an attractive destination for a diverse array of businesses.
The Real estate and investment
The real estate and investment sector in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a vital component of the country’s economy, known for its rapid growth and attracting both local and international investors. Here’s a more detailed overview of the UAE’s real estate and investment landscape, including its types and key characteristics:
Residential real estate: Residential real estate plays a significant role in the UAE financial system by contributing to economic growth and diversification. It serves as a magnet for local and international investments, with cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi offering a wide range of luxurious residential properties. This sector drives demand for construction, real estate services, and financing, bolstering the overall economy. Residential real estate in the UAE is closely tied to the influx of expatriates and tourists, as well as the government’s initiatives to develop world-class living spaces. Moreover, it is a source of government revenue through fees and taxes, and it underpins the broader real estate and financial markets, making it a vital component of the country’s economic landscape.
Commercial real estate: Commercial real estate plays a pivotal role in the UAE’s financial system, serving as a cornerstone for economic growth and diversification. It acts as a catalyst for attracting international businesses, investors, and entrepreneurs, making the UAE an attractive destination for foreign investments and trade. The sector encompasses office spaces, retail centers, industrial facilities, and logistics hubs, facilitating various industries and sectors. As one of the Middle East’s prime business and financial hubs, especially in cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi, commercial real estate not only provides physical infrastructure but also fosters economic activities, and job creation, and contributes significantly to the country’s GDP. The stability and growth of the commercial real estate market are closely intertwined with the overall financial stability and prosperity of the UAE.
Hospitality and tourism: Hospitality and tourism play a crucial role in the UAE’s financial system. The country is renowned as a global travel and leisure destination, attracting millions of visitors each year. This sector significantly contributes to the UAE’s GDP, creating jobs and stimulating economic growth. The UAE boasts iconic landmarks, luxurious hotels, world-class shopping, and cultural attractions, making it a preferred destination for both business and leisure travelers. The country’s strategic location as a transit hub further bolsters its appeal. With continuous investment in tourism infrastructure and hosting major international events, such as Expo 20202 (now Expo 2023), the hospitality and tourism industry is a linchpin of the UAE’s economic diversification and development strategy. It not only generates revenue but also supports other sectors like real estate, retail, and transportation, thus fueling the broader financial system.
Industrial and warehousing: Industrial and warehousing sectors play a crucial role in the UAE’s financial system. The country’s strategic geographic location at the crossroads of global trade routes has made it a major hub for logistics and trade. Industrial parks and warehousing facilities are essential components of this ecosystem, supporting the efficient movement and storage of goods. The UAE’s modern infrastructure, free zones, and business-friendly policies have attracted both domestic and international businesses, spurring investments in these sectors. This, in turn, drives economic growth, and job creation, and contributes significantly to the country’s overall financial stability, making industrial and warehousing pivotal elements of the UAE’s financial system.
Mixed-use developments: Mixed-use developments play a pivotal role in the UAE’s financial system by offering a diverse range of investment opportunities and contributing to economic growth. These developments combine residential, commercial, and retail spaces, creating vibrant urban centers that cater to both residents and businesses. They attract local and international investors, stimulate economic activity, and foster a sense of community. As integrated hubs, mixed-use developments enhance the utilization of real estate, boost rental yields, and stimulate consumer spending. In cities like Dubai, have become focal points for tourism, commerce, and lifestyle, driving demand for properties and bolstering the financial system through increased real estate transactions, business activities, and job opportunities.
Foreign Investments
Foreign investment in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has played a pivotal role in the country’s economic development. The UAE has actively sought to attract foreign capital and expertise across various sectors. Here’s a detailed yet brief overview of foreign investment in the UAE, including its types:
Direct Foreign Investment (FDI): Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) involves foreign individuals or entities making substantial investments in UAE-based companies. It can take the form of either acquiring a significant ownership stake in an existing company or establishing new business operations. The UAE has encouraged FDI by creating free zones that offer various incentives, such as full foreign ownership, tax exemptions, and streamlined administrative procedures. These zones, like the Jebel Ali Free Zone and Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), have attracted many foreign investors.
Portfolio Investment: Portfolio investment includes the purchase of shares, bonds, or other financial assets in UAE companies or government entities without seeking a controlling interest in these entities. Investors can participate in UAE stock markets (Dubai Financial Market and Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange) to engage in portfolio investment, potentially benefiting from capital gains and dividends.
Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs): The UAE manages several sovereign wealth funds, the most prominent being the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA) and the Investment Corporation of Dubai (ICD). These SWFs invest in a wide range of international assets, including equities, fixed-income securities, real estate, and infrastructure projects, helping the UAE diversify its investments globally.
Real Estate Investment: The UAE, particularly Dubai, has been a magnet for foreign real estate investment. Investors buy residential or commercial properties with the expectation of rental income and potential capital appreciation. Dubai, known for its luxury real estate market, has attracted investors from various parts of the world, contributing to the city’s skyline and economic development.
Infrastructure Investment: Foreign entities have the opportunity to participate in infrastructure projects in the UAE, including the construction and operation of roads, airports, ports, and utilities. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are common structures for infrastructure investment, allowing the private sector to collaborate with the UAE government on these projects.
Renewable Energy Investments: The UAE has shown a commitment to renewable energy, with projects such as large-scale solar and wind farms. These initiatives have piqued the interest of foreign companies and investors. The UAE aims to reduce its carbon footprint and diversify its energy sources by attracting foreign capital into renewable energy ventures.
Technology and Startups: The UAE has been actively fostering a thriving tech ecosystem. Foreign venture capital firms, technology companies, and angel investors are engaging with local startups. Hubs like Dubai Internet City and Dubai Knowledge Park provide platforms for innovation and growth in the tech sector.
Free Zones and Special Economic Zones: The UAE has established multiple free zones and special economic zones to attract foreign businesses. These zones offer unique advantages, including 100% foreign ownership, zero taxation, and simplified regulations. For instance, the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and the Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM) are home to many international financial institutions due to their favorable regulatory environments.
Trade and Manufacturing: Foreign investors often engage in trade and manufacturing activities in the UAE due to its strategic location as a global trade hub. The country’s excellent connectivity and world-class logistics infrastructure make it an ideal place for foreign companies to establish operations and expand their trade activities.
Tourism and Hospitality: The UAE’s tourism and hospitality sectors have attracted substantial foreign investment. Investors have been funding the development of hotels, resorts, theme parks, and entertainment facilities. Tourism is a significant driver of the UAE’s economy, with attractions like the Burj Khalifa, Palm Jumeirah, and various cultural and leisure destinations drawing millions of visitors each year.
The UAE’s commitment to diversifying its economy and encouraging foreign investment has created a vibrant and dynamic business environment, making it an attractive destination for investors across various industries. These investments have significantly contributed to the UAE’s economic growth and its position as a regional and global economic powerhouse.
Sovereign Wealth Funds
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) manages several sovereign wealth funds (SWFs), which are investment vehicles primarily funded by the government’s revenues, particularly from oil and other sources. These SWFs are created to invest in various assets, both domestically and internationally, to preserve and grow the nation’s wealth. Here’s a brief overview of the key UAE sovereign wealth funds and their types:

Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA): ADIA is one of the largest and most prominent sovereign wealth funds globally. It operates as a government-owned investment fund, primarily focused on long-term investments. ADIA was established to invest in Abu Dhabi’s oil revenues to ensure the country’s financial security and economic stability for future generations. ADIA has a diverse portfolio, including equities, fixed income, real estate, infrastructure, and alternative investments worldwide.

Investment Corporation of Dubai (ICD): ICD is a sovereign wealth fund wholly owned by the Government of Dubai. It was created to manage the government’s investments and promote economic development in Dubai. ICD has investments in various sectors, including finance, transportation, hospitality, real estate, and other key industries in Dubai.

Mubadala Investment Company: Mubadala is a government-owned investment fund that operates as a global investment and development company. It aims to diversify Abu Dhabi’s economy and create sustainable, long-term economic growth through investments in multiple sectors, including technology, aerospace, and healthcare. Mubadala’s investments span aerospace, semiconductors, renewable energy, healthcare, and technology, among others.
Emirates Investment Authority (EIA): EIA is the UAE’s federal sovereign wealth fund. It was established to invest federal government revenues and manage assets for the benefit of the UAE. EIA invests in various asset classes, including equities, fixed income, and real estate.
Ras Al Khaimah Investment Authority (RAKIA): RAKIA is the investment arm of the government of Ras Al Khaimah, one of the emirates of the UAE. It focuses on attracting foreign direct investments (FDI) to Ras Al Khaimah and managing local investments. RAKIA primarily invests in real estate, industrial projects, and infrastructure.
These sovereign wealth funds play a crucial role in managing and diversifying the UAE’s vast wealth, while also contributing to economic development and stability in their respective emirates and the country. Each fund has its specific investment focus and objectives, contributing to the UAE’s position as a global financial and investment hub.
Regulatory Framework
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has a well-established regulatory framework for its financial system, overseen by several key regulatory bodies. Here’s a brief overview of the regulatory framework and the primary financial regulatory bodies in the UAE:
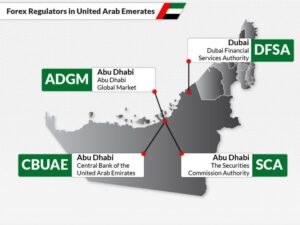
Central Bank of the UAE: The Central Bank of the UAE is the country’s central monetary authority, responsible for maintaining monetary stability and ensuring the soundness of the banking system. Its key functions include implementing monetary policy, issuing and managing the UAE Dirham (AED), and regulating and supervising commercial banks operating in the UAE. The Central Bank sets interest rates, manages foreign exchange reserves, and acts as the lender of last resort to maintain financial stability.

Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA): SCA is the primary regulatory body for the securities and commodities markets in the UAE. It regulates and supervises various aspects of the financial markets, including the activities of public joint-stock companies, stock exchanges, and securities trading. SCA’s mission is to ensure transparency and protect the interests of investors by enforcing regulations and market standards.
Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA): DFSA is an independent regulatory authority responsible for the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), a major financial free zone in Dubai. It sets and enforces regulations for financial and non-financial firms operating within the DIFC, ensuring compliance with international best practices. The DFSA’s main objective is to maintain the integrity and stability of the financial services industry within the DIFC.

Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM) Financial Services Regulatory Authority: ADGM Financial Services Regulatory Authority is the regulatory body for financial services activities in the Abu Dhabi Global Market, another significant financial free zone in the UAE. It oversees regulatory matters in the ADGM, ensuring that businesses and financial institutions adhere to relevant laws, regulations, and international standards.

Insurance Authority (IA): The Insurance Authority is responsible for the regulation and supervision of the insurance sector in the UAE. It establishes and enforces standards for insurance companies to ensure they provide fair and secure services to policyholders. IA’s mandate includes licensing, compliance, and consumer protection in the insurance industry.
UAE Ministry of Economy: While not a traditional regulatory body, the Ministry of Economy plays a vital role in formulating economic policies and legislation that affect the financial sector. It manages intellectual property rights, commercial affairs, and trade policies that contribute to the overall economic environment in the UAE.
Federal Tax Authority (FTA): The FTA is responsible for implementing and regulating the UAE’s tax framework, which includes value-added tax (VAT) and excise tax. It ensures compliance with tax laws and collects taxes from businesses and individuals to support government revenue.
Other Specialized Regulators: Depending on the specific financial activities, other specialized regulators may be involved. For example, the UAE Central Securities Depository (CSD) is responsible for overseeing the securities depository and settlement system, ensuring the efficient functioning of the stock market.
The regulatory framework in the UAE is comprehensive and designed to maintain financial stability, protect the interests of investors, and encourage business and financial sector growth. These regulatory bodies adapt to international standards and best practices to ensure the UAE remains an attractive destination for financial services and investments.
UAE Credit System
- Overview of the UAE Credit System
- Credit Score in UAE
- Credit Agencies in UAE
- Types of Credit Cards in UAE
- Sources of Credit Cards in UAE
- Types of Loans in UAE
Overview of the UAE Credit System
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) boasts a well-established and highly regulated credit system that underpins its robust financial industry. Governed by the UAE Central Bank and closely monitored by various financial institutions, this credit system is instrumental in facilitating lending and borrowing activities across the nation. Central to this system is the concept of credit scores and credit histories, which serve as the yardstick for evaluating an individual’s or business’s creditworthiness.
These scores consider various factors, including payment history, outstanding debts, the length of one’s credit history, the diversity of credit accounts, and the frequency of new credit applications. A favorable credit history can unlock access to an array of financial products, from loans to credit cards, while a less-than-favorable one can limit these opportunities. Ultimately, the UAE’s credit system is a cornerstone of its financial infrastructure, promoting responsible and transparent financial practices in the region. The UAE’s credit system is a cornerstone of its financial infrastructure, fostering responsible and transparent financial practices within the country.
Additionally, the UAE has implemented various consumer protection laws to safeguard the rights and interests of borrowers, promoting transparency and fairness in lending practices. The legal framework also includes regulations on interest rates, debt collection, and bankruptcy procedures, all aimed at maintaining the stability and integrity of the UAE’s credit system. Overall, the legal infrastructure surrounding the UAE’s credit system is designed to foster responsible and ethical financial conduct, benefiting both lenders and borrowers alike.
Role of UAE Central Bank in Credit System: The UAE Central Bank plays a central and vital role in the UAE’s credit system, serving as the principal regulatory authority and guardian of financial stability within the nation. It is responsible for formulating and implementing policies and regulations that govern the credit sector, ensuring it operates efficiently, transparently, and by international best practices. The Central Bank monitors and supervises the financial institutions, credit reporting agencies, and lending practices, safeguarding the interests of both borrowers and lenders.

It sets guidelines for credit reporting, guaranteeing the accuracy and reliability of credit reports, which are essential for evaluating the creditworthiness of individuals and businesses. Furthermore, the Central Bank can use its authority to influence interest rates and lending practices, impacting the cost and availability of credit to maintain economic stability. Overall, the UAE Central Bank’s role in the credit system is paramount in promoting a sound and secure financial environment in the United Arab Emirates.
Credit Score in UAE
A credit score, a three-digit figure that ranges between 300 to 900 in the UAE, is widely used as an indicator of your debt-paying capacity. It is often deployed by financial institutions to estimate the applicant’s creditworthiness and their behavior towards debt, past repayments, related risks, and any other type of default. As a good credit card score generally implies lower credit risk, lending institutions can find it easier to make decisions regarding credit card issuance, loan application processing, and other financial assistance to clients.

In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), this score is based on various financial behaviors, such as timely payments of loans and credit card bills, the management of outstanding debts, the length of one’s credit history, the types of credit accounts held, and the frequency of new credit applications. The credit score is typically computed by credit reporting agencies like the Al Etihad Credit Bureau, and it ranges from 300 to 900, with a higher score indicating a more favorable credit profile. A positive credit score opens doors to a range of financial opportunities, including favorable loan terms, credit cards with better perks, and more accessible financing. On the other hand, a lower credit score can limit access to credit or result in less favorable terms. Maintaining a healthy credit score is crucial in the UAE for obtaining financial services and achieving one’s financial goals.
The following is the general credit score range in the UAE:
| Credit Score Range | Credit Score Type |
| 300 to 619 | Bad Credit Score |
| 620 to 679 | Fair Credit Score |
| 680 to 730 | Good Credit Score |
| 731 and above | Excellent Credit Score |
Bad Credit Score: In the United Arab Emirates, a bad or poor credit score typically falls within the lower range of the credit scoring system, which may range from 300 to 619 depending on the specific credit reporting agency’s scoring model. A credit score in this range indicates a weaker credit profile and is associated with a history of financial challenges, such as late payments, defaults, high outstanding debts, and other negative financial behaviors.
Individuals with bad credit scores are considered higher credit risks by lenders and financial institutions. As a result, they may find it more challenging to qualify for loans, credit cards, or other financial products, and when they do, they may face less favorable terms, including higher interest rates and lower credit limits.
Fair Credit Score: A fair credit score typically falls within the middle range of the credit scoring system, which may vary depending on the specific credit reporting agency’s scoring model. While the specific score range can differ, a fair credit score often lies between 620 to 679.
A fair credit score indicates a moderate credit profile and suggests a history of mixed financial behavior. It may include a combination of positive financial habits, like timely payments and responsible credit management, along with some negative aspects, such as occasional late payments or higher credit card balances.
Good Credit Score: In the United Arab Emirates, a good credit score typically falls within the upper part of the credit scoring system, which often ranges from 680 to 730, although the specific range may vary slightly depending on the credit reporting agency. A good credit score reflects a strong credit profile, characterized by responsible financial behavior, such as consistent, timely payments, low outstanding debts, and a positive credit history.
Excellent Credit Score: In the United Arab Emirates, an excellent credit score typically falls within the highest range of the credit scoring system, which often spans from above 731 or a similar range. An excellent credit score signifies an exceptional credit profile, indicating an extensive history of responsible financial behavior, including consistently making payments on time, maintaining low outstanding debts, and possessing a strong and positive credit history.
Individuals with excellent credit scores are perceived as very low-risk borrowers by lenders and financial institutions. Consequently, they are more likely to qualify for loans, credit cards, and other financial products at the most favorable terms. Such terms may include lower interest rates, higher credit limits, and easier access to a wide range of financial opportunities.
Credit Agencies in UAE
Credit reporting agencies in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) play a crucial role in the country’s financial landscape by assessing and reporting on the creditworthiness of individuals and businesses. One of the primary credit reporting agencies in the UAE is the Al Etihad Credit Bureau (AECB). These agencies collect and maintain extensive data on individuals’ and entities’ credit histories, including information on loans, credit cards, and other financial obligations. This data is used to generate credit reports and scores that help lenders and financial institutions make informed decisions about extending credit.
By providing accurate and up-to-date information, credit reporting agencies promote transparency and responsible lending practices. They enable borrowers to build and maintain their credit profiles and allow lenders to assess risk more effectively, ensuring a healthier and more reliable financial ecosystem in the UAE. The work of credit reporting agencies is instrumental in facilitating access to credit and financial services while maintaining the integrity and stability of the financial sector in the UAE.
Al Etihad Credit Bureau: The Al Etihad Credit Bureau (AECB) in the United Arab Emirates is a prominent and government-regulated credit reporting agency that plays a pivotal role in the country’s financial landscape. Established in 2014, AECB serves as the primary source for credit information and credit reports for individuals and businesses in the UAE. AECB collects and compiles comprehensive data on credit histories, including loans, credit cards, and other financial obligations, from various financial institutions and lenders.

This data is then used to generate credit reports and credit scores for consumers and entities. AECB’s services provide transparency and credibility to the credit system, helping both borrowers and lenders make informed financial decisions. Individuals can access their credit reports to monitor their financial health, while lenders utilize AECB’s reports and scores to assess credit risk accurately. This contributes to responsible lending practices and fosters a stable and secure financial environment in the UAE.
AECB Credit Score: AECB credit score in UAE is calculated based on an aggregation of the following factors:
Payment History: The payment history on the credit card is undoubtedly the most important parameter to determine the AECB credit score of an individual. It is an objective record of all the payments that you have made timely or missed, and up to how recently payments have been made or missed. The score improves with a greater proportion of on-time payments. In case there is a significant delay in the payments extending to over 30 days, it is liable to be reported by the lender and it shall adversely impact the credit score UAE.
Length of Credit History: A good score is reflective of a history of making timely payments. Models that construct your score look at the average age of your credit when factoring in credit history.
Types of Accounts: Having a mix of accounts, whether they be retail or credit cards, would help improve your AECB credit score.
Recent Credit Activity: If the person has opened multiple accounts in recent times or submitted applications to open accounts, they could potentially come under the scanner. This can be perceived to be a sign of financial trouble and thus may lower AECB’s credit score.
Debt Accumulation: The second most important parameter is the amount that has been accumulated by way of loans on the credit card. This shall be based on the entire amount that is owed, and the proportion of money owed to the amount of credit that lies available in the card account.
Benefits of a Good AECB Credit Score: Does having a good credit score in UAE make life easier for you? The answer is a resounding yes. The benefits of maintaining a good AECB credit score far outweigh the cost of neglecting the same. Mentioned below are some of the lifestyle advantages that will accrue to you if you maintain a good score with due diligence:
The Low-Interest Rate on Credit Cards and Loans: If you are a businessman who has to constantly handle substantial flows of money from one point to another, small differences in interest rates could make a significant difference to the amount that you owe to creditors. A good AECB credit score will entitle you to lower interest rates, and this is strategically desirable from a business point of view.
Ease in Renting Apartments: A “fair credit range” comes in handy when searching for apartments for renting in a new city, since it shows reliability on the part of the prospective tenant. For instance, as per reports in 2019, the Dubai Real Estate Centre has decided to use the credit reports furnished by the Al Etihad Credit Bureau to evaluate the financial standing of the tenants. FAB Properties, which is part of the First Abu Dhabi Bank group, and is the real estate management arm of the same, has also been using the AECB’s data to assess tenants.
Reduced Car Insurance Premiums: Car owners with good scores have a better chance of receiving good offers on their car insurance premiums. Conversely, obtaining affordable car insurance with a poor score might turn out to be a challenge in some cases.
Employment opportunities: Employers might inquire about the credit score UAE of the job seeker among other things. A poor credit score might reflect a lack of financial discipline on the personal front, as well as a lack of seriousness when it comes to financial matters. A low credit score might reveal that the job seeker is in debt, and is struggling financially, which could affect their performance at work.
Factors That can affect your AECB Credit Score: AECB credit score UAE might be adversely affected by the following behaviors:
Late Payments: Even if one payment is delayed for more than 30 days, the credit score in UAE might suffer. The non-payment window is used to notify credit reporting bureaus of the delay, and this can adversely affect a UAE credit score.
Applying for more credit several times: Each time that you ask for credit, a hard credit inquiry shall be made on the account. Every hard inquiry shall affect the credit score in UAE, even when the approval is not granted.
Canceling your zero balance credit cards: If a cardholder decides to do away with a credit card, it might adversely affect their score. Cancelling a credit card reduces the total credit amount, which in turn increases the credit utilization ratio. It also shortens the credit history period.
Transferring the balances to a single card: It makes sense to carry just one credit card around, protecting against risks of theft, and general maintenance of multiple cards. However, transferring your credit balances consolidated into one card may not be advisable. The upward balance that will be created on the card will cause credit utilization to shoot up drastically, which will hurt the credit score in the UAE.
Giving authorization to relatives with unreliable credit scores: It is your choice if you wish to co-sign your account with a friend or a family member in need. Co-signing means you are responsible for their debt, and in case they default on payments from this account as well, you are bound to suffer a depreciation in your own UAE credit score.
Ways to Keep Your Credit Score Strong in UAE:
- Complete credit applications carefully and accurately.
- Use your credit cards responsibly, don’t let them reach their limit or spend beyond your means.
- Choose your credit cards and loans wisely and make sure you understand all of the terms and features.
- Pay your credit card balance in full each month, but at least make the minimum payment by the due date.
- Always pay bills on time.
- If you have problems paying your credit card balance or loan installments, contact your creditors. In many cases, they will work with you to figure out a payment plan.
- If you move, let your creditors know your new address as soon as possible to avoid losing bills or receiving them late.
- If your credit card is lost or stolen, report it to the issuer immediately.
- Check your credit report and score periodically. If you spot any inaccuracies, immediately report them to your banks to ensure your score is calculated correctly. In the UAE, you can get your score from the Al Etihad Credit Bureau (AECB) website, aecb.gov.ae, or by downloading the app, available in Google Play and Apple Store.
- Establish a consistent work history.
Types of Credit Cards in UAE
Credit cards in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) come in a variety of types to cater to diverse consumer needs and preferences. Common categories include standard credit cards, which offer a revolving credit limit for everyday purchases and come with varying features. Rewards credit cards provide cardholders with points, miles, or cashback for spending, which can be redeemed for travel, merchandise, or cash rebates. Travel credit cards are ideal for frequent travelers, offering benefits like airline miles, airport lounge access, and travel insurance. Cashback credit cards give a percentage of the spending back as cash, making them popular for saving on everyday expenses.
Premium or lifestyle credit cards provide exclusive privileges such as concierge services, luxury event access, and premium lounge access. Student credit cards are designed for young adults building their credit history, while business credit cards offer features tailored to company use. Islamic credit cards adhere to Sharia-compliant finance principles, and secured credit cards require a collateral deposit, helping individuals with limited or poor credit history build or rebuild their credit. The UAE’s credit card market is diverse, allowing consumers to select the card that aligns best with their financial goals and lifestyle.
Some common types of credit cards in the UAE include:
Standard Credit Cards: These cards provide a revolving credit limit that allows cardholders to make purchases and payments over time, offering flexibility for everyday spending needs. They typically come with a range of features, including varying interest rates, annual fees, and credit limits, catering to different financial profiles. Standard credit cards are suitable for individuals who want a straightforward and flexible payment option, offering the convenience of making purchases, paying bills, and covering unforeseen expenses while allowing for minimum monthly payments.
Cardholders can benefit from the convenience of credit cards, build their credit history, and enjoy added features like grace periods for interest-free spending when bills are paid in full each month. While they may not offer specialized rewards or exclusive perks like premium cards, standard credit cards are a practical choice for those seeking a fundamental and versatile financial tool in the UAE.
Rewards Credit Cards: These cards are designed to provide a variety of rewards, such as points, miles, or cashback, based on the cardholder’s spending habits. Cardholders can accumulate these rewards with each purchase and then redeem them for a range of benefits, including travel discounts, merchandise, gift cards, or even cash rebates. Rewards credit cards often come in different tiers, with higher-tier cards offering more lucrative benefits and exclusive privileges. These cards are an excellent choice for individuals who want to make the most of their everyday spending and enjoy perks like travel rewards, discounts, or cash savings, ultimately making them a valuable financial tool for those in the UAE looking to maximize their purchasing power.
Travel Credit Cards: These cards are designed to provide cardholders with an array of travel-related perks and benefits. Typically, they offer rewards in the form of airline miles, hotel stays, or travel points for each purchase, enabling cardholders to accumulate rewards to use towards future travel expenses. Travel credit cards often come with additional advantages such as airport lounge access, travel insurance, priority boarding, and exclusive discounts on flights and accommodations. For frequent travelers, these cards can be a valuable tool, making travel more affordable and enjoyable.
Cashback Credit Cards: These cards offer cardholders the opportunity to earn a percentage of the amount spent on purchases back as cash. The cashback is usually credited to the cardholder’s account or provided as a statement credit, effectively reducing the overall cost of their expenses. UAE consumers who use cashback credit cards often find them particularly beneficial for everyday spending, from groceries to dining and entertainment, as they can earn money back on these purchases. This makes these cards an attractive option for those seeking a practical way to save on their regular expenditures and enhance their overall financial well-being.
Premium or Lifestyle Credit Cards: These cards cater to high-income individuals and frequent spenders, providing a wide range of elite benefits and privileges. Cardholders of premium cards can expect features such as concierge services, access to luxury events and VIP experiences, premium airport lounge access, and personalized customer support. Some premium cards may also offer travel rewards, such as airline miles or hotel discounts, and generous cashback or reward programs. These cards are tailored to meet the demands of individuals who seek a higher level of service, prestige, and convenience, making them a symbol of luxury and sophistication in the UAE.
Student Credit Cards: These cards typically come with lower credit limits and often feature lower annual fees and interest rates compared to standard credit cards. Student credit cards aim to help individuals build their credit history responsibly while offering a practical means of managing their finances. These cards may come with educational resources on financial management, teaching students about budgeting and responsible credit use. While they may not offer extensive rewards or exclusive perks, student credit cards are an excellent starting point for those looking to establish their credit history and learn valuable financial skills.
Business Credit Cards: These cards are specifically tailored to meet the unique needs of businesses, providing a range of features that help manage expenses, track spending, and separate personal and business finances. Business credit cards often offer customizable spending limits, employee cards, and detailed expense reports, making it easier for companies to control costs and monitor their financial activities. Additionally, many business credit cards come with rewards programs that cater to business-related expenses, such as travel, office supplies, and telecommunications, enabling companies to earn valuable rewards on their spending.
Islamic Credit Cards: These cards are designed for individuals who prefer to avoid conventional interest-based transactions, which are considered “riba” or usury under Islamic law. Instead, Islamic credit cards follow a profit-and-loss sharing model, where the cardholder and the bank share in the profits and losses generated from the card’s activities. They do not charge or earn interest, and the fees are structured to comply with Islamic finance principles. Islamic credit cards may also offer ethical and charitable features, such as donating a percentage of the cardholder’s spending to charity. These cards provide a Sharia-compliant option for those who want to meet their financial needs while adhering to Islamic principles and beliefs in the UAE.
Secured Credit Cards: These cards require a security deposit, which serves as collateral against the credit limit. The deposit acts as a guarantee for the credit card issuer, making secured credit cards more accessible to those with limited or poor credit histories. By using a secured card responsibly and making timely payments, cardholders can gradually improve their credit scores over time. Secured credit cards offer an opportunity for financial rehabilitation and access to the world of credit, making them a practical choice for individuals who may not qualify for traditional credit cards due to past financial challenges.
Sources of Credit Cards in UAE
Credit cards in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) are primarily sourced through a combination of financial institutions, including local and international banks, credit unions, and non-bank financial institutions. These institutions issue credit cards to individuals and businesses based on their creditworthiness, financial history, and income levels. Customers can apply for credit cards through their chosen financial institution by applying, which is then evaluated by the issuing institution.
Many banks and financial institutions in the UAE offer a variety of credit card options, allowing customers to choose the one that best suits their spending habits and financial needs. Additionally, some credit cards may be offered through partnerships between banks and major retailers, providing specific benefits for shopping at those establishments. Customers can also access credit card information and apply online through the official websites of banks and financial institutions, streamlining the application process.
Banks: Banks are one of the primary sources of credit cards in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Both local and international banks operating in the UAE offer a wide range of credit card options to individuals and businesses. These banks assess applicants’ creditworthiness, financial history, and income levels when considering credit card applications. Customers can apply for credit cards through banks by submitting applications in person at branch locations or, more commonly, online through the banks’ official websites. Banks typically offer various types of credit cards, including standard, rewards, travel, cashback, and premium cards, among others, allowing customers to choose the one that aligns with their financial needs and preferences. These financial institutions play a crucial role in providing convenient and accessible credit options for UAE residents and businesses, contributing to the widespread use of credit cards in the country.
Some of the prominent banks that serve as sources of credit cards in the UAE include:
Emirates NBD is A leading bank in the UAE, offering a wide range of credit card options, from standard to premium cards.
First Abu Dhabi Bank (FAB) is One of the largest banks in the UAE, providing diverse credit card offerings with various features and benefits.
Mashreq Bank is Known for its innovative credit card products and rewards programs for customers in the UAE.
Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank (ADCB) Offers a selection of credit cards tailored to different customer needs and lifestyles.
Citi Bank UAE Provides credit cards with diverse rewards, including cashback and travel benefits.
RAKBANK Offers a range of credit cards designed to cater to various spending habits and preferences.
Standard Chartered UAE Offers credit cards with a variety of features, including rewards and cashback programs.
Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB) Offers Islamic credit cards that comply with Sharia principles.
HSBC UAE Provides credit cards with global acceptance and various rewards programs.
Union National Bank (UNB) Offers credit cards for individuals and businesses in the UAE.

Retailers:
In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), several major retailers and commercial entities offer co-branded credit cards that provide benefits, rewards, and discounts when used for purchases at their respective outlets. Some of the prominent retailers and entities that offer co-branded credit cards in the UAE include:
Carrefour This popular hypermarket chain has its co-branded credit card, offering discounts, rewards, and exclusive offers on groceries and other products.
Lulu Hypermarket Lulu offers a co-branded credit card with benefits like cashback and discounts at Lulu stores.
Emirates Co-operative Society (Union Coop) Union Coop offers its members a co-branded credit card with rewards, discounts, and exclusive promotions.
Majid Al Futtaim Properties This company offers a co-branded credit card for its properties, including malls like the Mall of the Emirates and City Centre.
Home Centre Home Centre has a co-branded credit card that provides discounts and benefits for purchases of furniture and home decor.
Sharaf DG The electronics retailer Sharaf DG offers a co-branded credit card with rewards and discounts on electronics and appliances.
Danube Home Danube Home has a co-branded credit card that offers benefits for furniture and home improvement purchases.

Airlines: In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), several airlines collaborate with banks to offer co-branded credit cards that provide travel rewards, frequent flyer miles, and exclusive benefits. These credit cards are tailored to travelers and aviation enthusiasts. Some of the airlines that offer co-branded credit cards in the UAE include:
Emirates Airlines Emirates partners with several banks to offer co-branded credit cards, such as the Emirates Skywards Credit Card, which allows cardholders to earn Skywards Miles for Emirates flights and other benefits like lounge access.
Etihad Airways Etihad Airways has co-branded credit cards that enable cardholders to earn Etihad Guest Miles, access airport lounges, and enjoy various travel privileges.
Flydubai Flydubai collaborates with financial institutions to provide co-branded credit cards, offering benefits like discounts on flights and duty-free shopping.

Hotel Chains: Several hotel chains partner with banks to offer co-branded credit cards that provide a range of hotel-related benefits, including free stays, room upgrades, and discounts. Some of the hotel chains that offer co-branded credit cards in the UAE include:
Hilton Hotels Hilton has co-branded credit cards in collaboration with local banks, offering rewards, Hilton Honors points, and complimentary hotel nights.
Marriott International Marriott has co-branded credit cards that allow cardholders to earn Marriott Bonvoy points, receive free hotel nights, and enjoy other Marriott-related benefits.
AccorHotels AccorHotels partners with banks to offer co-branded credit cards that provide rewards, Accor Live Limitless (ALL) points, and exclusive hotel privileges.
Rotana Hotels Rotana offers a co-branded credit card with benefits related to its hotel properties, including discounts, loyalty points, and other promotions.
Automobile Companies: Automobile companies in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) occasionally partner with banks to offer co-branded credit cards that provide benefits related to vehicle ownership, maintenance, and fuel purchases. While these partnerships may not be as common as those in other industries, some automobile companies have collaborated with banks to offer such credit cards. One example is:
Toyota UAE Toyota has partnered with some banks in the UAE to offer co-branded credit cards that provide benefits such as discounts on Toyota vehicle maintenance and services.
Telecom Companies: Telecom companies in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) sometimes collaborate with banks to offer co-branded credit cards that provide benefits related to mobile plans, data usage, and telecommunications services. While these partnerships are not as common as those in other industries, some telecom companies have worked with banks to provide such credit cards.
Etisalat UAE Etisalat, one of the major telecom providers in the UAE, has partnered with banks to offer co-branded credit cards that may include benefits like discounts on mobile plans, data rewards, and exclusive telecom-related privileges.
Types of Loans in UAE
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) offers a diverse range of loans to meet the financial needs of its residents and businesses. These loans encompass various categories, including personal loans, home loans (mortgages), auto loans, business loans, credit card loans, and Islamic finance products that adhere to Sharia-compliant principles. Personal loans are versatile, providing individuals with financial assistance for a variety of purposes. Home loans help people purchase property or real estate, with options available for both local and expatriate buyers. Auto loans assist in financing the purchase of new or used vehicles. Business loans cater to the financial requirements of entrepreneurs and companies.
Credit card loans allow cardholders to access cash advances, while Islamic finance products offer alternatives to conventional loans for those who prefer Sharia-compliant financing. Education loans and medical loans provide specific funding for education expenses and medical treatments, respectively. Overdraft facilities grant access to additional funds when needed, and short-term loans offer solutions for immediate financial needs.
Below are the different types of loans offered in the UAE market:
Open-Ended and Close-Ended Loans: Open-Ended Loans are kinds of loans that can be taken up by the borrower time and again. Credit cards, and bank overdrafts, among others, are some examples of open-ended loans. You are assigned a pre-set credit limit in your account. With every purchase or expenditure, the available credit limit or the loan limit is reduced. To make use of this credit again, the account owner has to repay the amount due along with the interest. Hence, once the dues are repaid you can again make use of the available credit.
Close-Ended Loans are loans that once repaid, cannot be used again. You will be required to apply for such loans again to enjoy the benefits. For example, if you take up a personal loan and repay the entire amount along with the fixed personal loan interest rate, you will be required to go through the entire application process again if you wish to reuse such funds.
Secured and Unsecured Ended Loans: Secured Ended Loans are loans that are backed by a guarantor, an asset, or collateral. If the borrower is unable to repay the entire amount, the lender can liquidate the asset to compensate for the loan repayment. Prime examples of such loans are mortgage loans or home loans. These are types of loans wherein the property or the house is provided as collateral or security against the loan amount. If the borrower is unable to repay the loan, the bank or institution can foreclose the loan and then adjust the amount.
Unsecured Loans are loans that do not require any collateral or underlying asset to secure them. All the financial institution or the bank gets is the borrower’s guarantee. A good example of such a loan is the personal loan in UAE, they do not require any security, and all that they need is the borrower’s guarantee against paying the loan amount at the fixed personal loan interest rate.
Auto Loans: These loans provide a convenient way to spread the cost of a vehicle over a set period, making it more affordable for buyers. Auto loans in the UAE come with different terms, interest rates, and financing options, allowing borrowers to select a loan that aligns with their specific preferences and budget. They typically require a down payment, and the vehicle itself may serve as collateral, making it a secured loan. Many banks and financial institutions in the UAE offer competitive auto loan products, and some even have partnerships with car dealerships for exclusive offers. Buyers can benefit from fixed interest rates, flexible repayment terms, and the convenience of owning a vehicle while making manageable monthly payments.
Business Loans: These loans are designed to provide businesses with essential capital for various purposes, including working capital, expansion, equipment purchases, and operational expenses. Business loans in the UAE can be structured in several forms, such as term loans, revolving lines of credit, or trade finance facilities, each tailored to meet specific financial requirements. Banks, financial institutions, and even government entities in the UAE offer business loans with competitive interest rates and terms. Additionally, Islamic banks provide Sharia-compliant business financing options to accommodate the preferences of businesses that adhere to Islamic finance principles. These loans serve as a lifeline for businesses, enabling them to thrive, invest in growth opportunities, and contribute to the dynamic and ever-evolving economy of the UAE.
Islamic Finance Products: Islamic finance products in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) offer Sharia-compliant alternatives to conventional loans for individuals and businesses. These products adhere to Islamic finance principles, which prohibit interest (riba) and require financial transactions to be based on profit-and-loss sharing, ethical investments, and asset-backed arrangements. Some common Islamic finance products in the UAE include Islamic personal loans, home financing (Ijara), and business financing (Musharakah). Islamic banks in the UAE provide these products, allowing customers to access funding without violating Islamic ethics. Islamic finance products are well-suited for individuals and businesses seeking ethical and interest-free financial solutions.
Medical Loans: These loans are especially valuable for individuals facing unexpected medical costs or those seeking medical treatments not covered by insurance. Medical loans are typically unsecured, meaning they do not require collateral, and they come with fixed or variable interest rates, depending on the lender. The UAE’s competitive financial sector offers medical loans with flexible repayment terms to suit various budgets and healthcare needs. This type of financing allows patients to access necessary medical care without compromising their financial well-being and ensures that high-quality healthcare services are within reach for residents in the UAE.
UAE Education System
- Overview of the UAE Education System
- Structure of the UAE School System
- Types of Schools
- Enrollment in School
Overview of the UAE Education System
The education system in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has undergone significant transformation and expansion over the past few decades, making it a key component of the country’s vision for a diversified and knowledge-based economy. The UAE’s education system is governed by the Ministry of Education, with each of the seven emirates having its educational authorities to manage and oversee schools within their jurisdictions. Education is compulsory for Emirati children from the age of six to eighteen, and the government has made substantial investments in building state-of-the-art schools, colleges, and universities.
The UAE places a strong emphasis on providing quality education, with a focus on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects. Furthermore, the country has attracted prestigious international universities, fostering a diverse and multicultural academic environment. The education system in the UAE aims to prepare students for the challenges of a rapidly changing global economy, ensuring they have the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in an increasingly competitive world.
Ministry of Education: Established in 1971, the Ministry is responsible for overseeing and regulating the education sector across all seven emirates, working in collaboration with local educational authorities to maintain high standards and consistency in education. The Ministry of Education is tasked with developing educational policies, curricula, and standards, as well as providing support and resources for schools and educational institutions. The Ministry of Education’s dedication to providing quality education is instrumental in realizing the UAE’s goal of becoming a knowledge-based economy and ensuring that the nation’s students are well-prepared to meet the challenges of the future.
Since investing in human capital is the main objective, the UAE has been keen on establishing the Ministry of Education and creating the appropriate environment to build pioneering Emirati schools, in terms of standards, form, and content they provide. It also made sure that such schools provided high-quality educational environments and owned the most technically advanced tools to be able to graduate generations that were capable of pursuing their university education confidently in higher education institutions. It is worth mentioning of course that such higher education intuitions have undergone a massive development and update process in terms of quantity and quality. It started with the opening of the mother United Arab Emirates University and then the Higher Colleges of Technology, followed by the opening of the Zayed University in Abu Dhabi and Dubai. The opening of private and government higher education institutions has continued ever since, to serve as incubators of innovation for the country’s young people. They have also been provided with new academic majors that fulfill the requirements of the labor market.
The MoE has also provided a smart learning system and high-quality digital platforms, side by side with the continuous development of school curriculums, according to national learning standards, assessment policy that is based on assessing for learning, and highest quality standards that match the best international practices. Various learning tracks, moreover, have been provided to support the capabilities and skills of students and achieve the country’s strategy of encouraging the culture of creativity and innovation by providing the students with the skills of the 21st century and motivating them to have new ideas that relate to the reality they live in and foresee the future. This will eventually help in finding radical, sustainable solutions to the major issues, improving competitiveness, and supporting smart government in its attempts to keep pace with global advancements, advance education, and push it to broad horizons of excellence, leadership, and competitiveness.

Structure of the UAE School System
The school system in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) follows a well-structured framework designed to provide a comprehensive and quality education to students. The system is divided into four main levels: primary education, middle education, secondary or technical education, and Tertiary Education which includes Bachelor, Master, or Doctorate. Both public and private schools operate across the UAE, offering a diverse range of curricula, including international ones, to cater to the nation’s multicultural population. Overall, the structured school system in the UAE aims to equip students with the skills and knowledge necessary for personal growth and success in a globalized world.
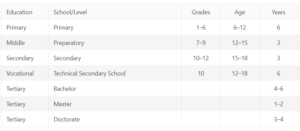
Primary Education: Primary education in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a fundamental stage of the country’s education system, typically catering to students between the ages of 6 to 12 and with grade levels of 1 to 6. It spans a six-year cycle and plays a crucial role in providing students with a strong foundation in essential subjects. The primary education curriculum in the UAE emphasizes subjects such as Arabic, English, mathematics, science, social studies, and physical education. Students are also introduced to the culture and history of the UAE, promoting a sense of national identity. The primary education system in the UAE strives to create a nurturing and inclusive environment, supporting students’ growth and development, and preparing them for a seamless transition into secondary education.
Primary education in the UAE aims to develop students’ cognitive, social, and emotional skills, along with nurturing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. The education system places a strong emphasis on technology and innovation, ensuring that students are well-prepared for the challenges of a rapidly evolving world. Primary education is compulsory for Emirati children, and the UAE government has invested significantly in building modern and well-equipped schools, as well as providing professional development opportunities for teachers to maintain high educational standards.

Middle Education: Middle education is an essential phase in the country’s education system, catering to students typically between the ages of 12 to 15 and grades of 7 to 9. Middle education bridges the gap between primary and secondary education, providing a well-rounded foundation for further academic pursuits. This level of education is also known as preparatory education, and it spans a three-year cycle.
Middle education in the UAE builds upon the knowledge and skills acquired during primary education, and it introduces a more specialized curriculum to prepare students for the challenges of secondary education. Subjects covered during this phase include Arabic, English, mathematics, science, social studies, and physical education, as well as elective courses to cater to individual interests and aptitudes. The curriculum is designed to foster critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills, equipping students with a strong academic base.

Secondary Education: Secondary education in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a vital stage in the country’s education system, serving students typically between the ages of 15 to 18 and grades 10 to 12. It is a three-year cycle that prepares students for higher education or the workforce. Secondary education follows the General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) system and successful completion of this level leads to the attainment of the UAE High School Certificate.
The secondary education curriculum in the UAE is comprehensive and challenging, designed to provide students with a well-rounded education. It includes subjects such as Arabic, English, mathematics, science, social studies, and physical education. Students have the opportunity to choose elective courses, allowing them to focus on areas of interest and aptitude. Additionally, secondary education places a strong emphasis on career guidance, helping students make informed decisions about their future academic and professional paths.

Vocational Education: Vocational education, often referred to as technical and vocational education and training (TVET), is designed to equip students with practical skills and knowledge that are directly relevant to the job market. It is an alternative to Secondary Education serving students typically between the ages of 12 to 18 and grades 10. It offers an alternative pathway for students who may not pursue traditional academic education. Vocational education programs in the UAE cover a diverse array of fields, including healthcare, engineering, information technology, hospitality, tourism, and many other sectors. These programs are typically available at vocational training centers, technical colleges, and through partnerships with industry-specific institutions. Vocational education in the UAE emphasizes hands-on learning, internships, and apprenticeships to ensure that students gain real-world experience in their chosen fields.

Tertiary Education: It encompasses higher education institutions, including universities, colleges, and vocational schools, and is designed to provide students with opportunities for advanced learning and specialization in a wide range of academic and professional fields. The UAE has made significant investments in its tertiary education system, both by establishing world-class universities and by attracting prestigious international institutions. These institutions offer a broad spectrum of programs, including undergraduate and postgraduate degrees in areas such as business, engineering, science, medicine, humanities, and the arts.
Tertiary education includes a Bachelor which is of 4 to 6 years then a Master’s level which is of 1 to 2 years and the last Doctorate level which is also ranges from 3 to 4 years. Tertiary education in the UAE places a strong emphasis on research, innovation, and technology. The country is committed to fostering a culture of knowledge and discovery, and this is reflected in the research initiatives, state-of-the-art facilities, and partnerships with global institutions. The UAE government has also introduced scholarship programs to attract top talent from around the world, making it a hub for international students seeking a high-quality education.

Types of Schools
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) boasts a diverse landscape of educational institutions, catering to the needs of its multicultural population. There are several types of schools in the UAE, including government-run public schools, private schools, and international schools. Public schools provide education to Emirati citizens and follow the UAE national curriculum, emphasizing Arabic language and Islamic studies. Private schools, on the other hand, cater to both Emirati and expatriate communities and may offer various international curricula, including British, American, Indian, or the International Baccalaureate (IB).
These schools often provide a higher degree of flexibility and choice in terms of curriculum. International schools, while also private, predominantly serve the expatriate population and typically follow the curriculum of their home country. These schools offer a seamless transition for students who may return to their home countries for further education.

Different types of Schools in the UAE include:
Public Schools: Public schools in the UAE are government-funded educational institutions that serve as a cornerstone of the country’s education system. These schools primarily cater to Emirati citizens and play a pivotal role in preserving the cultural and religious heritage of the nation. The UAE national curriculum, which emphasizes Arabic language and Islamic studies, forms the foundation of the education provided in these institutions. Public schools offer free education to Emirati students, including not only tuition but also textbooks and, in many cases, transportation.
The UAE government has made substantial investments in these schools, ensuring that they are equipped with modern facilities, including cutting-edge classrooms, laboratories, and sports facilities. The goal is to maintain high educational standards and prepare Emirati students for leadership roles in various sectors, contributing to the country’s “Emiratization” process.
Private or International Schools: These institutions cater to both Emirati and expatriate communities, providing an alternative to the UAE national curriculum typically offered in public schools. Private schools in the UAE often follow international curricula, such as British, American, Indian, or the International Baccalaureate (IB), allowing students to access a world-class education while residing in the country. This diversity in curriculum and teaching approach provides families with the flexibility to choose an educational program that aligns with their cultural, academic, and career aspirations.
Private schools in the UAE are known for their modern facilities, state-of-the-art resources, and highly qualified teachers. While private education comes at a cost, it offers a wide range of extracurricular activities and enrichment programs, making them attractive options for those seeking a well-rounded and globally-focused education in the UAE.
The most famous top private schools in UAE are:
- The Indian High School
- GEMS Wellington International School
- Deira International School
- RAK Academy
- The International School of Choueifat
- Al Dhafra Private Schools
- American School of Creative Science
Special Needs Schools: These schools are an integral part of the UAE’s commitment to inclusivity and ensuring that all students, regardless of their abilities, have access to quality education. Special needs schools in the UAE offer individualized learning plans and therapeutic services that address a wide range of disabilities, including autism, dyslexia, cognitive impairments, and physical disabilities. Highly trained educators and specialists work in these schools to create a nurturing and inclusive environment where students can thrive and develop their full potential.
The UAE government has made substantial efforts to promote the inclusion of students with special needs in mainstream schools as well, but special needs schools continue to play a critical role in providing comprehensive and targeted support for students with disabilities. These institutions contribute significantly to enhancing the quality of life and opportunities for individuals with special needs in the UAE.
The most famous top special needs schools in UAE are:
- Dubai Center for Special Needs
- Mohammed bin Rashid Center for Special Education
- Emirates Autism Center
- Special Needs Future Development Center
Military and Police Schools: These schools offer a unique and disciplined educational environment, reflecting the values and principles of the UAE’s armed forces and security services. Students in these schools receive not only a standard academic curriculum but also specialized training in areas such as leadership, discipline, and physical fitness. The focus on character development, teamwork, and a strong work ethic is central to their educational approach.
These schools play a crucial role in preparing students to follow in the footsteps of their family members in the military and law enforcement fields, instilling a strong sense of patriotism and a commitment to serving their country. Additionally, these institutions often provide a path to careers within the military or police forces, contributing to the nation’s security and defense efforts while promoting a sense of duty and national pride among their students.
Several military institutions have been established to provide military education and knowledge. Some of them are:
- Joint Command and Staff College
- Zayed the Second Military Academy
- Khalifa Air College
- Nursing School
- The Khawla bint Al Azwar Military School (KBAS)
- National Defense College.
Enrollment in School
Enrolling in schools in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) follows a systematic and organized procedure that reflects the country’s commitment to offering quality education to its diverse and multicultural population. Parents and guardians seeking to enroll their children in UAE schools, whether public or private, typically begin by submitting the necessary documents, including a child’s passport, residency visa, birth certificate, health records, and academic transcripts.
The UAE’s education system is known for its inclusivity, accommodating the linguistic and cultural preferences of the expatriate community, which makes up a significant portion of the student population. Many expatriates choose to enroll their children in private or international schools, each of which may have its specific enrollment process. These schools may require additional documentation and assessments to determine the student’s eligibility and grade placement. The enrollment process in the UAE aligns with the nation’s vision of providing a world-class education system, fostering an environment where students can thrive and succeed in an ever-evolving global landscape.
Enrollment in Public School: Parents or legal guardians of Emirati students typically begin the enrollment process by submitting essential documents, such as a child’s birth certificate, passport, residency visa, health records, and academic transcripts. These documents are important for verifying a student’s eligibility and age for a particular grade level. In public schools, the curriculum predominantly follows the UAE national curriculum, emphasizing Arabic language and Islamic studies, reflecting the cultural and religious values of the country.
The UAE government generously funds public education, providing Emirati students with free schooling, including tuition, textbooks, and often transportation. These schools have witnessed significant developments, with modern and well-equipped facilities, classrooms, and resources to ensure students have access to a high-quality education. The enrollment process for public schools in the UAE aligns with the nation’s vision of fostering an educated and knowledgeable citizenry, equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary for personal and national success.
The UAE offers free school education to:
- The UAE nationals
- Holders of the UAE passports
- GCC citizens
- The children of holders of nationality by decrees issued by the UAE’s President or the Vice President.
Expatriate students are permitted to attend public schools on payment of 6,000 AED as tuition fees and subject to certain conditions. The conditions include:
- Expatriate students may be admitted in grades 2 to 12
- The student’s parent should hold a job in a government, semi-government, or local entity
- The student’s grade should not be below 85 percent in Arabic language, English language, and Mathematics
- The student and his parent must have a valid UAE residence visa
- Expatriate students should not exceed 20 percent of the total capacity in each public school and each classroom.
The language of instruction in the UAE’s public schools is Arabic for all subjects. The schools follow the Emirati national curriculum approved and supervised completely by the Ministry of Education.
Enrollment in Private Schools: Enrolling in private schools in the UAE follows a relatively straightforward yet structured process, reflecting the country’s commitment to providing a diverse and high-quality education. Parents or guardians typically initiate the enrollment process by contacting their chosen private school and submitting the required documentation, which may include a child’s birth certificate, passport, residency visa, health records, and academic transcripts.
Private schools in the UAE often offer various international curricula, such as British, American, Indian, or the International Baccalaureate (IB), allowing families to choose an educational program that aligns with their cultural and academic preferences. These schools may have their specific enrollment requirements, including entrance exams, interviews, or placement assessments to determine the student’s eligibility and appropriate grade level. While private education in the UAE comes at a cost, these schools offer modern facilities, well-qualified teachers, and a wide range of extracurricular activities, making them attractive options for those seeking a well-rounded and globally-focused education.
Enrollment in Special Needs Schools: Special needs schools in the UAE are equipped to address a wide range of disabilities, such as autism, dyslexia, cognitive impairments, and physical disabilities. These institutions offer specialized programs, individualized learning plans, and therapeutic services to meet each student’s specific needs. Parents or guardians typically initiate the enrollment process by contacting the chosen special needs school and providing the necessary documentation, which may include the child’s birth certificate, passport, residency visa, medical records, and an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) or relevant assessment reports.
The enrollment process often involves an initial assessment or meeting with the school’s staff to determine the student’s eligibility and create an appropriate educational plan. Parents or guardians work closely with the school to ensure that the child’s unique requirements are met. The UAE government promotes inclusivity and aims to offer students with special needs a nurturing and supportive educational environment, where they can thrive and reach their full potential.
Enrollment in Military or Police School: Enrollment in these schools is generally limited to students from military or law enforcement families, ensuring a close-knit community and a shared commitment to service and duty. These institutions instill a strong sense of patriotism and prepare students for potential careers within the military or police forces, emphasizing qualities like leadership, teamwork, and a deep sense of national pride. The enrollment process varies by institution, but it’s typically open to eligible children of military and police personnel, further contributing to the UAE’s security and defense efforts.
Military and police schools in the UAE offer a unique and disciplined educational environment that reflects the values, principles, and traditions of the UAE’s armed forces and security services. In addition to a standard academic curriculum, these schools often provide specialized training in areas such as leadership, discipline, physical fitness, and national service preparation.
UAE Health Care System
- Overview of the UAE Health Care System
- Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP) UAE
- Health Care Providers in UAE
- Components & Coverage of UAE Health Insurance
- Types of Health Insurance
- Health Care Regulation
Overview of the UAE Health Care System
The healthcare system in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is known for its rapid development and high standards of care. The UAE government places a significant emphasis on providing accessible, comprehensive, and high-quality healthcare services to its residents and citizens. The system comprises a mix of public and private healthcare facilities, with both sectors contributing to the overall healthcare infrastructure. The public healthcare system is largely funded and managed by the government, offering affordable and often free services to Emirati citizens. Public hospitals and clinics are equipped with state-of-the-art technology and staffed by well-trained medical professionals.
The private healthcare sector, on the other hand, caters to a significant portion of the population, including expatriates, offering a wide range of medical services and specialties. The UAE has also made substantial investments in medical tourism, attracting patients worldwide seeking advanced medical treatments and procedures. With its commitment to healthcare, the UAE ensures that its residents have access to world-class medical care, making it a key player in the region’s healthcare landscape.
The healthcare system in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is primarily under the oversight and regulation of the UAE Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP). However, healthcare management and delivery can vary between the different emirates within the UAE. Each emirate may have its health authority or health department responsible for managing and delivering healthcare services at the local level. For example, Dubai has the Dubai Health Authority (DHA), Abu Dhabi has the Department of Health Abu Dhabi, and so on.
These local health authorities collaborate with the federal MOHAP to ensure a high standard of healthcare across the country. The UAE strongly emphasizes providing accessible and high-quality healthcare services to its residents and citizens, regardless of their nationality or background.
Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP) UAE:
MOHAP is entrusted with the responsibility of safeguarding and promoting the health and well-being of the nation’s population. The ministry is involved in various healthcare functions, including the development of healthcare policies, the regulation of medical services, the promotion of public health, and health education. MOHAP works tirelessly to ensure that healthcare services are of the highest quality and accessible to all residents and citizens.
Since the creation of the UAE’s union on December 2, 1971, the country’s health sector has witnessed great qualitative accomplishments in a bid to meet various health challenges and keep pace with global developments. From day one, the UAE recognized the importance and necessity of making the most of all advanced technologies and resources to improve this vital sector, while providing an appropriate health environment, believing that promoting the lives of its people is the end goal and main focus of development, to help them fulfill their national responsibilities, and contribute effectively to the process of development.
The health sector is one of the most developed in the UAE, and ranks first worldwide across several approved health indicators, thanks to following a health system based on the highest international standard in addition to developing the readiness of the health system to deal with pandemics and health risks, which made the country one of the best countries in the quality of healthcare.
The ministry has also adopted a methodology that applies the highest standards of excellence and professionalism, built state-of-the-art hospitals equipped with the latest equipment across the country, and highly experienced medical staff, and launched several campaigns to enhance health awareness of the community. The national health strategy also reflects the UAE’s interest in the health sector.
From applying international standards in infrastructure management in health facilities to building quality systems and safety therapeutic, health, and pharmaceutical systems by international standards and providing a vital legislative framework and governance, the ministry has been keen to develop health information systems and provide regulatory and oversight services to the health sector.
In addition, the UAE is geared towards artificial intelligence and digital medical services. The Ministry of Health and Prevention has developed a comprehensive plan to integrate artificial intelligence 100% into medical services, in line with the UAE’s AI Strategy, by the UAE’s 2071 centenary to transform patient healthcare.

Health Care Providers in UAE
These providers include public and private hospitals, clinics, specialized medical centers, and a rapidly expanding network of healthcare professionals. The UAE boasts a thriving private healthcare sector, with a multitude of private hospitals and clinics that provide comprehensive and specialized medical services, often with a focus on international standards and state-of-the-art facilities. Public healthcare, managed by the UAE Ministry of Health and Prevention and local health authorities, offers accessible and affordable medical services to Emirati citizens.
The country also attracts a significant number of skilled healthcare professionals and specialists from around the world, contributing to the overall quality and diversity of healthcare services. The UAE’s healthcare system prioritizes both preventive and curative care, aiming to ensure that residents and citizens receive top-tier medical attention and that the nation maintains high healthcare standards, making it a key player in the region’s healthcare landscape.
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) boasts a robust healthcare sector with a wide range of healthcare providers, including:
Public Hospitals and Clinics: These institutions fall under the purview of the UAE Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP) and local health authorities in each emirate. Public hospitals and clinics offer a wide range of healthcare services, from general medical care to specialized treatments, often equipped with state-of-the-art technology and staffed by highly qualified healthcare professionals.
Public healthcare in the UAE is characterized by a strong emphasis on preventive care, with regular screenings, vaccinations, and health education programs being an integral part of the services provided. This approach aligns with the country’s vision of maintaining the health and well-being of its citizens. Emirati citizens typically receive these healthcare services at a significantly reduced cost, with many services being offered free of charge. These public healthcare providers also contribute to medical research and training, often in collaboration with international institutions, further enhancing the quality of healthcare in the UAE.
Private Hospitals and Clinics: These healthcare providers offer a diverse array of medical services and specialties, catering to both UAE residents and the expatriate population. Known for their advanced technology, modern facilities, and international standards of care, private hospitals and clinics play a vital role in enhancing the overall quality of healthcare services in the UAE. Patients seeking medical care in private healthcare institutions benefit from a wide range of specialties, including cardiology, orthopedics, oncology, and more. Moreover, these hospitals often attract highly qualified medical professionals and specialists from around the world, making the UAE a hub for medical talent.
The private healthcare sector in the UAE is committed to providing patient-centered care, often with shorter waiting times and a more extensive range of elective and specialized procedures. Patients in these facilities often have the option to choose their physicians and take advantage of luxurious amenities, creating a more personalized and comfortable healthcare experience.
Specialized Medical Centers: These centers are dedicated to specific medical fields and offer specialized expertise, state-of-the-art technology, and a multidisciplinary approach to patient care. Some of the most common specialized medical centers in the UAE focus on areas such as cancer treatment, cardiac care, fertility treatments, and orthopedics. These institutions are known for their commitment to research, innovation, and patient outcomes.
For instance, cancer centers in the UAE offer comprehensive oncology services, including diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care, often following international best practices. Cardiac centers provide advanced treatments and procedures for heart-related conditions. Fertility clinics offer solutions for couples struggling with infertility, and orthopedic centers specialize in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders.
Primary Care Clinics: These clinics offer general medical care, routine check-ups, preventive services, and the management of common health issues. Primary care physicians play a critical role in promoting public health and well-being by providing early diagnosis and treatment, as well as offering guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle. In addition to addressing immediate healthcare needs, these clinics often deliver vaccinations, maternal and child health services, and chronic disease management.
UAE residents and expatriates can access primary care clinics throughout the country, and these facilities are typically the initial step in the healthcare system. The primary care system is well-structured and emphasizes a patient-centered approach, where individuals can build long-term relationships with their healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and the management of chronic conditions.
Dental Clinics: These clinics offer a wide range of treatments, from routine dental check-ups and cleanings to more specialized services such as orthodontics, oral surgery, and cosmetic dentistry. Dental care is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, and the UAE places a strong emphasis on oral health. Dental clinics in the UAE are known for their modern facilities, state-of-the-art equipment, and highly qualified dental professionals. The country boasts a strong network of dental professionals, including general dentists, orthodontists, oral surgeons, periodontists, and prosthodontists, ensuring that patients have access to comprehensive dental care.
Oral health is not only about maintaining a beautiful smile but also plays a significant role in overall health. Regular dental check-ups and preventative measures are vital in preventing and addressing dental issues early, reducing the risk of more severe problems.
Pharmacies: Pharmacists in the UAE are highly trained and play a vital role in ensuring the safe and effective use of medications. They offer valuable services such as medication counseling, dosage instructions, and guidance on potential side effects or interactions. Additionally, many pharmacies in the UAE offer immunization services, health screenings, and chronic disease management programs, contributing to the overall health and well-being of the community.
Pharmacies are easily accessible throughout the UAE, often located in residential neighborhoods and shopping centers. They serve a diverse and multicultural population, and many pharmacists are multilingual, accommodating the linguistic preferences of the expatriate community.
These services offer remote medical consultations and healthcare advice, often facilitated through digital platforms and mobile apps. Telemedicine providers connect patients with healthcare professionals through virtual consultations, offering a range of medical services, from general medical advice to specialized care. This approach aligns with the UAE’s commitment to innovation and technology, making healthcare accessible and convenient for its diverse and tech-savvy population.
Telemedicine services have proven particularly valuable in the UAE, as they address issues such as access to healthcare in remote areas, reduced wait times for consultations, and convenient follow-up care. Moreover, the services have played a crucial role in addressing healthcare challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, minimizing in-person contact while ensuring that patients continue to receive the care and advice they need.
Home Healthcare Services: These services are essential for individuals who require ongoing care, such as the elderly, those with chronic conditions, or patients recovering from surgeries. Home
healthcare providers typically offer a wide range of services, including nursing care, medication management, wound care, physical therapy, and assistance with activities of daily living.
Home healthcare services are valued for their patient-centered approach, enabling individuals to receive personalized care that caters to their specific needs. They provide a solution for patients who prefer the familiarity and comfort of their home environment over institutional care. Moreover, home healthcare services can be a cost-effective and efficient way to deliver medical care while reducing the strain on hospital resources.
Components & Coverage of UAE Health Insurance
Health insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) comprises several essential components that together ensure comprehensive healthcare coverage for residents and expatriates. These components encompass a range of services and benefits, including inpatient and outpatient care, emergency services, maternity and newborn care, chronic condition management, and preventive care. Health insurance plans in the UAE also extend coverage to specialist consultations, prescription medications, dental and optical services, and a network of healthcare providers.
Additionally, policyholders have the flexibility to choose optional add-ons to tailor their coverage, such as additional coverage for alternative therapies or international medical services. These components of UAE health insurance reflect the country’s commitment to providing accessible and high-quality healthcare services, thereby promoting the health and well-being of its diverse population.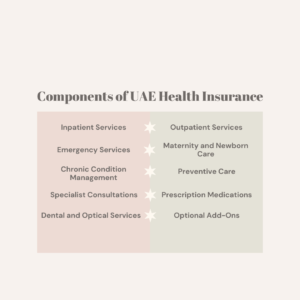
The key components of UAE health insurance include:
Inpatient Services: This coverage ensures that policyholders have access to necessary medical care when they require hospitalization. Inpatient services under UAE health insurance typically encompass a broad range of medical treatments and interventions, including surgeries, intensive care, diagnostic tests, and specialized medical procedures that necessitate hospital stays. The coverage extends to hospital-related expenses, such as room and board, operating room charges, and physician fees, thereby alleviating the financial burden on patients during hospitalization.
Outpatient Services: These services cover doctor’s consultations, diagnostic tests, treatments, and medical procedures that do not require hospitalization. UAE health insurance policies typically include coverage for outpatient care, allowing individuals to seek medical attention, diagnosis, and treatment for various health issues.
Emergency Services: This coverage encompasses various emergency medical services, including ambulance transportation and emergency room treatment. In a healthcare landscape where, unexpected medical emergencies can arise, having access to timely and effective emergency services is essential for saving lives and providing immediate care. UAE health insurance policies typically include coverage for these services, reflecting the nation’s commitment to safeguarding the health and well-being of its residents and visitors.
Maternity and Newborn Care: UAE health insurance policies typically include comprehensive maternity coverage, encompassing prenatal care, childbirth, postnatal care, and care for the newborn. This coverage ensures that expectant mothers receive the necessary medical attention and support throughout their pregnancy and childbirth journey, making it more affordable and accessible. By including newborn care, health insurance also extends its protection to the newest members of the family, covering essential healthcare services during the critical early stages of an infant’s life.
Chronic Condition Management: UAE health insurance policies typically include benefits that encompass medications, regular check-ups, specialist consultations, and diagnostic tests needed for effectively managing these long-term health issues. By doing so, health insurance aims to enhance the quality of life for individuals with chronic conditions, minimize the financial burden associated with ongoing medical care, and ensure that they have the support they need to lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
Preventive Care: This coverage typically includes essential services such as vaccinations, health screenings, and wellness programs aimed at identifying health issues before they become more severe or chronic. Preventive care is a cornerstone of the UAE’s healthcare system, contributing to the overall health and well-being of its residents and expatriates. By encouraging regular check-ups, vaccinations, and lifestyle modifications, health insurance promotes a culture of health-consciousness, helping individuals stay healthier and reducing the burden on the healthcare system.
Specialist Consultations: This coverage ensures that individuals can seek the specialized care they need without significant financial barriers, ultimately contributing to their overall health and well-being. Specialist consultations play a vital role in early diagnosis, advanced treatment, and better health outcomes, aligning with the UAE’s commitment to providing comprehensive and accessible healthcare services.
Prescription Medications: This coverage encompasses the cost of medications, making them more affordable and accessible for policyholders. UAE health insurance policies typically cover a wide range of prescription medications, including those for acute conditions, chronic diseases, and specialized treatments. By including prescription medication coverage, health insurance helps individuals manage their health conditions effectively, adhering to prescribed treatment plans without the financial burden of expensive medications.
Dental and Optical Services: UAE health insurance policies often offer optional coverage for dental and optical care, encompassing services such as routine check-ups, dental treatments, vision tests, and eyeglasses or contact lenses. These services recognize the significant impact of oral and visual health on overall well-being and quality of life. By including dental and optical coverage, health insurance ensures that individuals have access to necessary preventive and corrective care for their teeth and eyes, ultimately contributing to their overall health and comfort.
UAE health insurance policies typically offer a range of optional add-ons that individuals and families can choose to include in their coverage. These add-ons can encompass various services, such as alternative therapies, international medical services, access to specialized medical centers, or additional benefits for specific medical conditions.
Types of Health Insurance
In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), several types of health insurance plans are available to cater to the diverse healthcare needs of residents and expatriates. The most common types of health insurance in the UAE include:

Basic Health Insurance: Basic health insurance, often referred to as the Essential Benefits Plan (EBP), is a mandatory type of health insurance for all residents and expatriates in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). It serves as the foundation of the country’s healthcare system, providing essential coverage for medical services. While the exact benefits may vary slightly depending on the emirate and the insurance provider, EBP typically includes coverage for inpatient care, emergency services, and access to a network of healthcare providers. While this insurance offers fundamental coverage, individuals often have the option to enhance their plans by opting for additional coverage and services, catering to their specific healthcare needs.
Comprehensive Health Insurance: Comprehensive health insurance is a widely sought-after type of coverage in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), offering a broad range of benefits to policyholders. These policies provide extensive coverage for various healthcare services, including inpatient and outpatient care, maternity and newborn care, dental and optical services, and often a more substantial network of healthcare providers. Comprehensive health insurance is popular among residents and expatriates who seek a higher level of protection and a more inclusive healthcare package. These policies are known for their flexibility and can be tailored to meet specific healthcare needs, making them a valuable choice for those who prioritize comprehensive medical care and peace of mind.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance: Employers in the UAE often provide health insurance to their employees and, in some cases, to their employees’ dependents. These policies are designed to ensure that employees have access to quality healthcare services, covering a wide range of medical needs, from routine check-ups to specialized treatments. It not only contributes to the well-being of the workforce but also aligns with the UAE’s vision of offering comprehensive healthcare services to all residents and expatriates, emphasizing the importance of health and wellness in the nation’s workforce.
Family Health Insurance: These policies are tailored to cover spouses and dependent children, ensuring that the entire family has access to a wide range of medical services, including inpatient and outpatient care, maternity and pediatric services, and dental, and optical care. Family health insurance offers peace of mind by addressing the unique healthcare needs of each family member. It reflects the UAE’s commitment to promoting the well-being of families and aligns with the nation’s vision of comprehensive healthcare services.
Individual Health Insurance: These policies are designed to provide personal health coverage and can be customized to align with an individual’s unique requirements. Individual health insurance in the UAE typically offers a range of benefits, including inpatient and outpatient care, preventive services, and specialist consultations. It provides a level of independence and choice, allowing policyholders to select the coverage and services that best meet their health and financial needs.
Travel Health Insurance: These policies offer protection and peace of mind for individuals who are temporarily in the UAE for business or leisure purposes. Travel health insurance typically
covers a range of medical services, including emergency medical treatment, hospitalization, and repatriation to the home country in case of a severe medical emergency. These policies ensure that travelers have access to healthcare services during their stay in the UAE and help them navigate unforeseen health issues while away from their home country.
Senior Health Insurance: Senior health insurance recognizes that older individuals may require more frequent medical attention and access to specific healthcare services. It plays a critical role in ensuring that seniors have the financial protection and support needed to maintain their health and well-being. These policies often include coverage for chronic disease management, regular check-ups, and access to a network of healthcare providers who specialize in senior care.
Critical Illness Insurance: These policies offer coverage for a predetermined list of critical illnesses, such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. In the event of a critical illness diagnosis, policyholders receive a lump-sum payment that can be used for medical treatments, living expenses, or any other needs. Critical illness insurance serves as a safety net, ensuring that individuals and their families are financially secure during challenging times and can focus on their recovery without the added burden of medical expenses.
Health Care Regulation
The UAE’s healthcare system is overseen by several key entities, including the UAE Ministry of Health and Prevention and individual emirate-level health authorities, such as the Dubai Health Authority (DHA) and the Abu Dhabi Health Services Company (SEHA). These regulatory bodies establish and enforce standards for healthcare facilities, healthcare professionals, and medical practices, promoting excellence and adherence to best practices. They oversee licensing and accreditation processes, monitor healthcare quality, and implement healthcare policies to maintain patient safety and ensure that the healthcare system aligns with international standards. The UAE places a strong emphasis on healthcare regulation to guarantee that residents and visitors have access to reliable and effective healthcare services while upholding the nation’s reputation as a leading regional healthcare hub.
Key stakeholders in healthcare regulation in the UAE include:
UAE Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP): MOHAP is responsible for developing comprehensive healthcare strategies, promoting public health, and ensuring that healthcare services across the UAE meet international standards of quality and safety. The ministry also collaborates with emirate-level health authorities, such as the Dubai Health Authority (DHA) and the Abu Dhabi Health Services Company (SEHA), to align and coordinate healthcare regulations and policies at the federal and emirate levels.
Emirate-Level Health Authorities: Emirate-level health authorities, such as the Dubai Health Authority (DHA) and the Abu Dhabi Health Services Company (SEHA), are crucial stakeholders in healthcare regulation within the United Arab Emirates (UAE). They are responsible for developing local health strategies, ensuring compliance with federal regulations, and overseeing healthcare facilities and professionals. These authorities collaborate with the UAE Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP) to maintain consistent and high-quality healthcare standards across the country while addressing specific healthcare challenges at the emirate level.
Professional Licensing Bodies: These organizations, such as the Dubai Health Authority’s Regulation and Licensing Department, have a critical role in ensuring the competence and qualifications of healthcare professionals practicing in the country. They oversee the licensing, credentialing, and regulation of physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and allied healthcare providers. These bodies establish rigorous standards and guidelines for professional practice, ensuring that healthcare professionals maintain high levels of competency and adhere to ethical and professional conduct. Their work guarantees that patients in the UAE receive healthcare services from well-trained and qualified professionals who meet the country’s rigorous healthcare standards.
Healthcare Professionals: These individuals are directly impacted by healthcare regulations and standards, which influence how they provide care and interact with patients. Healthcare professionals are required to adhere to licensing and credentialing requirements, maintain the highest standards of clinical practice, and follow ethical guidelines. They play a crucial role in ensuring the delivery of quality, safe, and ethical healthcare services, thus upholding the country’s reputation as a regional healthcare hub.
Health Insurance Providers: These companies, which offer health insurance policies to individuals and organizations, are closely regulated to ensure that their policies provide comprehensive and accessible coverage for medical services. Health insurance providers must comply with the regulatory guidelines and standards set by the UAE’s health authorities to safeguard the interests of policyholders. Their role is crucial in supporting the UAE’s mandate for mandatory health insurance, which ensures that all residents and expatriates have access to essential medical care. The regulations governing health insurance providers include rules related to policy coverage, claim processing, and adherence to contractual agreements.
UAE Insurance System
- Overview of the UAE Insurance System
- Types of Insurance in UAE
- Health Insurance
- Life Insurance
- Motor Insurance
- Property and Casualty Insurance
- Travel Insurance
- Business Insurance
- Pet Insurance
Overview of the UAE Insurance System
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) boasts a well-developed and dynamic insurance system that serves the diverse needs of its residents and businesses. The insurance sector in the UAE is regulated by the UAE Insurance Authority, which oversees and enforces the rules and regulations governing insurance companies and brokers. The UAE insurance system offers a wide array of coverage options, including health insurance, life insurance, property and casualty insurance, motor insurance, and more.
Health insurance is mandatory for all residents, ensuring that individuals have access to essential medical care. The country’s insurance industry is known for its stability and adherence to international standards, making it a reliable destination for investors and policyholders. The UAE’s vibrant economy and growing population contribute to the expansion and diversification of its insurance sector, positioning the country as a key player in the regional insurance market. The UAE’s insurance system also offers investment opportunities, driven by the country’s economic stability and strong regulatory framework. Emirate-level regulations complement federal oversight, particularly in health insurance and healthcare practices. By collaborating with international organizations, the UAE aligns its insurance practices with global standards, further solidifying its position as a regional insurance hub.

Types of Insurance in UAE
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) offers a diverse range of insurance products to cater to the needs of its residents and businesses. Some of the prominent types of insurance in the UAE include:

Health Insurance and its Types: Health insurance is a crucial component of the insurance landscape in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). It holds particular significance in the UAE due to its mandatory nature, which reflects the country’s commitment to ensuring access to healthcare for all residents and expatriates. Health insurance policies in the UAE are comprehensive, covering a wide range of medical expenses, from routine check-ups and doctor’s visits to hospitalization, surgical procedures, diagnostic tests, and preventive care. Many policies also include maternity care and pediatric services, catering to families and individuals.
One noteworthy aspect of health insurance in the UAE is the inclusion of coverage for pre-existing conditions. This means that individuals with ongoing health issues or chronic conditions can access the necessary medical care without facing prohibitive costs. Health insurance not only provides financial protection but also enhances the overall quality of healthcare services by promoting early diagnosis and preventive measures.
The UAE’s health insurance system contributes significantly to the nation’s reputation as a regional healthcare hub, offering access to high-quality medical care and ensuring that residents and expatriates alike can benefit from a robust and inclusive healthcare system. The mandatory nature of health insurance underscores the UAE’s vision of accessible and comprehensive healthcare services for all.

Some well-known Health insurance providers in the UAE are:
- Daman
- AXA Gulf
- Gulf Insurance Group (GIG)
- MetLife Alico
- Dubai Insurance Company (DIC)
- Salama Islamic Arab Insurance
- AETNA International
Several types of health insurance plans are available in the UAE to cater to the diverse healthcare needs of nationals and expatriates. We talk in detail about types of Health Insurance in the Health Care portion. It includes:
- Basic Health Insurance
- Comprehensive Health Insurance
- Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
- Family Health Insurance
- Individual Health Insurance
- Travel Health Insurance
- Senior Health Insurance
- Critical Illness Insurance
Life Insurance and its Types: Life insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) serves as a financial safety net for individuals and families, offering protection and peace of mind. Life insurance policies in the UAE are designed to provide financial support to beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder’s death. These policies can be tailored to suit a variety of needs, such as income replacement for the family, paying off outstanding debts, covering education expenses for children, or even serving as a form of investment with savings and retirement planning components. Life insurance helps ensure that loved ones are financially secure and can maintain their quality of life in challenging circumstances. It also serves as a crucial estate planning tool, allowing for the orderly transfer of assets and wealth to heirs. With various insurance providers offering a range of life insurance options, residents in the UAE can select policies that align with their unique financial goals and family needs.
Some notable Life insurance providers in the UAE are:

In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), there are several types of life insurance policies available to residents. These policies cater to a range of financial needs and goals. Some of the common types of life insurance in the UAE include:
Term Life Insurance: Term life insurance offers coverage for a specified term, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. If the policyholder passes away during the term, a death benefit is paid to the beneficiaries. It provides affordable protection and is often used to cover temporary financial obligations, such as a mortgage or children’s education.
Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage, as long as premiums are paid. It also includes a cash value component that grows over time and can be accessed or borrowed against. Whole life insurance offers both protection and a savings or investment element.
Universal Life Insurance: Universal life insurance combines lifelong protection with flexibility in premium payments and the potential to adjust the death benefit and cash value. It allows policyholders to manage their coverage to meet changing financial needs.
Endowment Insurance: Endowment policies provide a death benefit to beneficiaries if the policyholder passes away during the term, similar to term life insurance. However, if the policyholder survives the term, they receive a lump-sum payout, making it a combination of insurance and savings.
Critical Illness Insurance: Critical illness policies pay a lump sum upon diagnosis of a covered critical illness, offering financial protection during a health crisis. It is not limited to death benefits and can help cover medical expenses and lifestyle adjustments.
Savings and Investment-Linked Insurance: These policies combine life insurance with an investment component. A portion of the premium is allocated to investments, such as mutual funds or stocks, allowing policyholders to potentially grow their wealth.
Group Life Insurance: Group life insurance is typically provided by employers for their employees. It offers a death benefit to the beneficiaries of covered employees and maybe a basic employee benefit.
Islamic or Takaful Insurance: Takaful life insurance is compliant with Islamic finance principles and operates on a cooperative basis, where policyholders share in the profits and losses of the fund. It offers Sharia-compliant protection and savings options.
Motor Insurance and its Types: Motor insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is not only a legal requirement but also an essential safeguard for vehicle owners. Known as compulsory third-party liability insurance, this type of insurance is mandatory for all vehicles in the UAE. It provides coverage for bodily injury or death to third parties in the event of an accident. While this basic coverage is required by law, vehicle owners can also opt for comprehensive motor insurance. Comprehensive motor insurance not only covers third-party liability but also protects one’s vehicle against theft, accidents, and damage. With the high number of vehicles on the UAE’s roads, motor insurance plays a crucial role in ensuring that drivers and their vehicles are financially protected in case of unforeseen events. It offers peace of mind and allows vehicle owners to meet their legal obligations while securing their assets against potential risks.
Some notable Life insurance providers in the UAE are:

In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), there are several types of motor insurance policies designed to meet the diverse needs of vehicle owners. These policies offer different levels of coverage, allowing individuals to select the one that best suits their requirements. Some of the common types of motor insurance in the UAE include:
Third-Party Liability Insurance: Third-party car insurance covers all the damages, accidentally caused to a third-party vehicle by you. However, third-party liability insurance does not cover any damages incurred by your vehicle. Third-party car insurance in the UAE is basic and obligatory auto insurance, mandated by the law. Third-party car insurance, also known as third-party liability insurance (TPL), is generally economical compared to a comprehensive car insurance policy.
Comprehensive Insurance: Comprehensive motor insurance is the most extensive type of coverage. It includes protection from third-party liability as well as damage to the policyholder’s vehicle due to accidents, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters.
Third-Party Fire and Theft Insurance: This type of insurance offers coverage for third-party liability, as well as protection against damage to the policyholder’s vehicle due to fire or theft.
Own Damage Insurance: As the name suggests, own damage plans are designed to cover the repair expenses for damages incurred by your car. Think of third-party liability car insurance plans and comprehensive plans. Own damage car insurance plans fall somewhere in between both these types. A comprehensive car insurance plan is made by combining its damage and third-party insurance. Having just your damaged car insurance cover for your vehicle means that your insurance provider will not cover the damages caused to the third-party car or the driver.
Agency Repair Insurance: The Agency repair cover benefit is an insurance benefit for your car that allows you to get your car repaired at the agency or dealership from where you bought the car. This means you are entitled to get your repairs done by manufacturer-certified technicians and the complete cost is covered by the insurance company, minus the deductibles. Needless to say, agency repairs are expensive because every emirate in the UAE generally has only one dealer for each manufacturer.
Off-Road Insurance: Off-road insurance is designed for those who engage in desert driving and provides coverage for damage that may occur during off-road adventures.
GCC Extension: Some policies include coverage in other Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, making it suitable for those who frequently travel to neighboring countries.
Roadside Assistance: Roadside Assistance in car insurance or RSA cover is one of these elements. It offers help or assistance if the car of the policyholder happens to break down while driving on an unfamiliar road or when there are no mechanics near the site of the breakdown. Roadside assistance cover is often offered as an inclusive part of the basic insurance cover while others offer it as an add-on benefit like engine protection cover, car accessory cover, etc.
Rental Car Coverage: This option covers the cost of renting a replacement vehicle while the insured vehicle is being repaired after an accident. This insurance coverage means that you should take it in case you are renting a car in the UAE. This type of car insurance plan is usually offered by car rental companies at the time of the rental process.
Property and Casualty Insurance and its Types: `Property and casualty insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) offers protection against a wide range of perils, including damage or loss of property, liability claims, and other unforeseen events. Property insurance covers assets such as homes, businesses, and personal belongings against perils like fire, theft, and natural disasters. Casualty insurance, on the other hand, protects against liability claims, including those related to bodily injury or property damage to third parties. This dual coverage ensures that individuals and businesses are financially safeguarded against potential losses, accidents, and legal liabilities. Whether it’s safeguarding a family home or protecting a business from legal claims, property, and casualty insurance plays a crucial role in providing peace of mind and financial security in the face of unexpected events.
Property and casualty insurance is key to ensuring your business’ success both now and in the future. It ensures that you’ve covered all bases when it comes to business risks and exposures and that any unforeseen incidents don’t cost you an arm and a leg. In business terms, this means you’ll avoid a dent in your balance sheet that ultimately causes you to cease your business operations.
Some notable Property and Casualty insurance providers in the UAE are:
- RSA Insurance
- Salama Islamic Arab Insurance
- Dubai Insurance Company (DIC)
- Gulf Insurance Group (GIG)

Property and casualty insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) encompasses various types of coverage to protect against property damage and liability claims. Some common types of property and casualty insurance in the UAE include:
Home Insurance: Homeowners insurance provides coverage for residential properties, protecting against risks like fire, theft, natural disasters, and vandalism. It also covers personal belongings and provides liability protection.
Commercial Property Insurance: This type of insurance is tailored for businesses, offering coverage for commercial properties, equipment, inventory, and other assets. It safeguards against property damage and business interruption.
Liability Insurance: Liability insurance offers protection against legal claims and lawsuits. This can include general liability insurance for businesses and personal liability coverage.
Marine Insurance: Marine insurance covers cargo and vessels, protecting against risks during shipping and transportation. It is particularly important for the UAE’s bustling maritime trade.
Aviation Insurance: Aviation insurance provides coverage for aircraft, airlines, and aviation-related risks. Given the UAE’s significant role in aviation and the presence of major airlines, this insurance is crucial.
Professional Liability Insurance: Professional liability insurance, also known as errors and omissions insurance, is essential for professionals like doctors, lawyers, and consultants to protect against malpractice claims.
Event Insurance: Event insurance is crucial for those organizing events or exhibitions. It covers risks related to event cancellations, accidents, and liability claims.
Construction and Engineering Insurance: This insurance provides coverage for construction projects and engineering works, protecting against construction delays and potential damage.
Travel Insurance and its Types: Travel insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) plays a significant role in ensuring peace of mind for travelers embarking on journeys, whether for leisure or business. This form of insurance offers a safety net against unexpected events that can disrupt travel plans. Travel insurance typically covers a range of scenarios, including trip cancellations, delays, lost baggage, medical emergencies, and even emergency evacuation. In a country known for its extensive international travel, UAE residents often seek travel insurance to mitigate the financial risks associated with travel-related mishaps. This type of insurance ensures that individuals and families can explore the world with confidence, knowing that they have protection in place should unforeseen events occur, making it a crucial component of responsible travel planning.
The UAE emphasizes every individual traveling abroad holding valid travel insurance. Additionally, travelers visiting the UAE are required to purchase a travel insurance UAE plan that covers their trips’ emergencies and medical expenses in case of accidents.
The United Arab Emirates has an extensive travel insurance market offering a variety of plans designed as per the travelers’ changing requirements. For instance, several insurers offer multi-trip insurance for frequent travelers, with the plans being capable of being modified as per changing plans. Alternatively, you can opt for single-trip insurance if your itinerary is fixed or likely to remain the same. Purchasing a travelling insurance plan in the UAE is fairly easy, and you get both online and offline options for choosing the best travel insurance in the UAE as per your needs. A few vulnerabilities covered under Travel Insurance UAE are as follows.
- Travel inconveniences and accidents,
- Baggage loss and delays,
- Flight cancellations and delays,
- Personal accidents and emergency hospitalization,
- Evacuations and Repatriations.
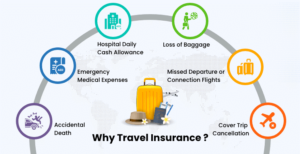
Some notable Travel insurance providers in the UAE are:
Travel insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) comes in various forms to cater to the diverse needs of travelers. Some common types of travel insurance available in the UAE include:
Single Trip Travel Insurance: A single trip travel insurance plan is designed to cover individual trips that you take within UAE or outside to other countries. Available in many forms and shapes, one-trip travel insurance plans are ideal for people who go on trips once a year, or twice at max. The plan coverage begins as soon as you buy the plan and ends when you are back to your home from the trip. You can easily find single-trip insurance plans for yourself as an individual, for family, for business trips, for international travels as well as domestic trips.
Annual or Multi-Trip Travel Insurance: An annual multi-trip travel insurance plan is one of the most common travel insurance online plans. It is designed to cover multiple trips taken within the tenure of the plan instead of just one. Ideal for people who travel multiple times within a year for work or other purposes, an annual multi-trip travel insurance plan serves as a very cost-effective option. Whether it is your family that you visit often in a year or travel for work, an annual multi-trip plan can be a good option for you to choose.
Schengen Travel Insurance: Travel across the Schengen countries without the worry of incurring any emergency medical expense, trip cancellation, or baggage luggage loss at the airport. Schengen Travel Insurance has got you covered as you travel across 26 European countries. You can enjoy the scenic views of the Eiffel Tower, The Leaning Tower of Pisa, and the surreal countryside without the worry of unforeseen events during the trip. The best part is that people with Schengen Travel Insurance usually get a Schengen Visa earlier than those who do not have one.
Business Travel Insurance: Business travel insurance, similar to personal travel insurance, aims to provide comprehensive security for your trips. These plans are specifically designed for businesses by analyzing their travel requirements, the threats and eventualities they may encounter during a business trip, and the implications of such incidents for them.
Several insurance providers in the UAE offer business travel insurance at nominal premiums and provide extensive security against travel accidents, medical emergencies, and trip inconveniences like baggage loss, credit card fraud, etc. As a business traveler, you can opt for single-trip insurance or purchase multi-trip travel insurance for the whole year to secure all your yearly trips in a single plan.
Student Travel Insurance: Essentially, it is a type of international travel insurance plan that is designed for students planning to study abroad. It covers all the basic aspects that a normal travel insurance plan covers along with a few added ones that may be beneficial to students. It is a unique mix of many different types of general insurance plans, mainly travel and health. From medical expenses to personal liability, trip and baggage benefits, and sponsor protection. The tenure of a student travel insurance plan can range from 1 to 2 years including any extensions you apply for.
Adventure or Sports Travel Insurance: Extreme sports collectively refer to adventurous and high-risk sports. Extreme sports travel insurance in UAE is explicitly designed to provide coverage to UAE residents traveling specifically with the motive of engaging in extreme sports. As mentioned earlier, standard travel insurance plans in the UAE generally don’t cover extreme sports.
Consequently, extreme sports travel insurance becomes an excellent option for short-term coverage for individuals planning to experience the thrill of extreme adventures and sports.
Senior Travel Insurance: Senior citizen travel insurance, as implied by the name, is a type of travel insurance that specifically provides coverage to individuals above the age of 65 on a trip. If any of your elderly family member over 65 years of age is traveling, it is required to purchase a travel insurance policy to get them covered against any mishaps during the trip.
Group Travel Insurance: A group travel insurance plan is a type of travel insurance plan designed to cover a group of travelers under a single policy. With group travel insurance, you can find similar benefits as any generic travel insurance plan. If you are traveling with a group of people with the same travel itinerary, you can take a group travel insurance plan instead of taking multiple individual ones.
Islamic or Takaful Travel Insurance: Takaful is a term that encompasses the idea of Islamic insurance, which operates on the principle of cooperation. In this system, both the insured individuals and the insurer share risks and funds. Takaful travel insurance is compliant with Islamic finance principles, making it suitable for travelers who prefer Sharia-compliant insurance options.
Cruise Travel Insurance: All insurance companies across the world offer insurance policies to financially secure your trips and journeys. Cruise travel insurance is a subcategory of travel insurance. While spending your holidays on a cruise is pleasurable, it is always advisable to purchase travel insurance for cruise trips. This type of plan includes numerous coverages that provide compensation for accidents, medical emergencies, cruise delays or cancellations, loss or delay of luggage, and so on.
Business Insurance and its Types: Business insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a crucial component of risk management for companies of all sizes and across various industries. It provides financial protection and safeguards against potential setbacks that can disrupt operations or lead to substantial financial losses. Business insurance encompasses a wide range of coverage options, including property insurance to protect assets, liability insurance to address legal claims, and specialized policies to cover industry-specific risks.
Companies in the UAE often invest in business insurance to mitigate the financial impact of events like fire, theft, liability lawsuits, and business interruption. In a dynamic and competitive business environment like the UAE, having the right insurance coverage is essential for ensuring that companies can continue to thrive, even when unforeseen events occur. This insurance is a valuable tool that offers peace of mind and financial security, allowing businesses to focus on growth and success with confidence.

Business insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) encompasses various types of coverage to address the unique needs and risks faced by different industries. Some common types of business insurance in the UAE include:
Property Insurance: This coverage protects a business’s physical assets, including buildings, equipment, inventory, and other property, from risks such as fire, theft, natural disasters, and vandalism.
Liability Insurance: Liability insurance safeguards businesses against legal claims and lawsuits. This includes general liability insurance, product liability insurance, and professional liability insurance (e.g., errors and omissions insurance).
Business Interruption Insurance: Business interruption insurance is a type of liability insurance coverage that helps replace business money or income that suffered a direct physical loss or damage due to some sort of disaster, maybe fire or any natural disaster. These insurance plans mainly cover claims due to flood, fire, and property-related physical damages that might result in destructive impacts, theft, and vandalism.
Commercial Vehicle Insurance: This insurance is essential for businesses with a fleet of vehicles. It covers company-owned vehicles against accidents, theft, and damage. Commercial vehicle insurance is physical damage and liability protection for vehicles that are used for business and commercial purposes. Buying commercial vehicle insurance is important as it protects your assets and property in case of an accident or unforeseen event.
Workers’ Compensation Insurance: Workers Compensation, also referred to as Workers Comp, is a type of insurance designed to provide wage replacement and medical benefits to employees who face any injuries while on the job during working hours. By purchasing Workers’ Compensation Insurance, a company can easily cover the costs of medical care, lost wages, and other benefits for injured workers.
Cyber Insurance: Cyber Risk Insurance, also known as Cyber Liability Insurance or Cyber Insurance, is a type of insurance that protects businesses from risks associated with network and data security, breach of privacy, and other cybersecurity-related issues. Cyber Risk Management Insurance also covers the financial damages incurred by you (first-party losses) or your clients (third-party losses) in case of a data breach or any other cyber crime against your organization.
Marine Insurance: Marine insurance is a contract of indemnification that guarantees that the products shipped from the country of origin to the destination country are fully insured. Any loss or damage to ships, cargo, terminals, and other transportation modes used to ship or acquire products between their points of origin and their destination is compensated by marine insurance.
Professional Indemnity Insurance: Professional Indemnity Insurance (PI insurance), also known as Errors and Omissions insurance (E&O) protects professionals against claims made by clients for damages caused due to professional negligence or errors in their work. Professional indemnity is essential for anyone who offers advice or provides a service. Professional Indemnity Insurance UAE and other countries can provide coverage for the legal costs of defending a claim and any awarded damages.
Directors and Officers (D&O) Insurance: Directors’ and officers’ insurance, also known as D&O insurance, is a type of liability insurance that protects the directors and officers of a company from legal action taken against them due to their actions or decisions as leaders of the organization. This type of insurance is particularly important in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) as the country’s business environment can be complex and litigious. With the start-up ecosystem picking up pace and investments coming in, having a D&O policy becomes mandatory.
Pet Insurance and its Types: Pet insurance is a special type of insurance for various animals that safeguards their overall health and well-being. Just like we buy health insurance for ourselves and our loved ones, insurance for pets has become a great way to provide for our pets if they happen to need medical and other financial help. Pet insurance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is an emerging and increasingly popular service that provides pet owners with financial protection and peace of mind when it comes to their beloved furry or feathered companions.
As pets are considered cherished members of many households in the UAE, pet insurance helps cover the costs of veterinary care, surgeries, medications, and other medical treatments for pets. Additionally, pet insurance may offer coverage for boarding fees, lost pet advertising, and even liability in case a pet causes harm or damage to others. With the rise in pet ownership and awareness of the importance of responsible pet care, pet insurance in the UAE is becoming an essential tool for pet owners to ensure that their pets receive the best possible care and attention in case of unexpected health issues or emergencies. This type of insurance not only eases the financial burden but also promotes responsible pet ownership, contributing to the well-being of pets and their owners alike.
Why Would I Need Pet Insurance? Already a thriving practice abroad, pet insurance in UAE has been gaining popularity thanks to a range of benefits it brings:
Ensures Best Health: Your precious pets will get the best treatment and medical care thanks to the insurance policy
Affordable and Saves Extra Expenses: By investing just a small premium, your pet can get covered for a range of benefits including medical care, accidents, and even overseas protection in many cases!
Safeguard from Accidents: While we can’t peel our eyes away from our furry babies, they sometimes get hurt while playing or because of other reasons. Your insurance will cover all these
medical expenses so that you don’t burn a hole in your pocket.
Other Benefits: Depending on your insurer, your pet will get exclusive benefits like coverage for third-party damages, or your pet getting stolen.

There are various types of pet insurance available to cater to the diverse needs of pet owners in the UAE, including:
Accident-Only Insurance: This type of pet insurance covers injuries resulting from accidents such as car accidents, falls, or other sudden mishaps. It typically doesn’t cover illnesses or routine veterinary care.
Illness Insurance: Illness insurance provides coverage for veterinary bills related to illnesses that may affect your pet, such as infections, allergies, or chronic conditions.
Comprehensive Coverage: Comprehensive pet insurance combines accident and illness coverage, offering a broader range of protection for your pet. It includes both accident-related injuries
and illnesses.
Wellness Plans: Some pet insurance providers offer wellness plans that cover routine veterinary care, including vaccinations, annual check-ups, and preventative treatments. This helps pet owners manage the costs of routine pet healthcare.
Cancer Coverage: Specialized pet insurance policies may cover cancer treatments for pets, including chemotherapy, surgery, and medication, as cancer treatment can be a significant expense.
Hereditary and Congenital Conditions Coverage: This type of insurance covers health conditions that are genetically or congenitally inherited by your pet, ensuring they receive the necessary treatment.
Lifetime Coverage: Lifetime pet insurance offers continuous coverage for your pet throughout its life, provided you renew the policy each year. This type of insurance ensures that chronic conditions are covered over time.
Third-Party Liability Insurance: This form of pet insurance protects you in case your pet causes harm or damage to others, including legal liability coverage for accidents or incidents involving your pet.
Lost Pet Insurance: Some pet insurance policies offer coverage for advertising and reward costs to help find your pet if it goes missing.
UAE Housing System
- Overview of the UAE Housing System
- Entities Involved in the UAE Housing System
- Types of Houses in UAE
- Ways to Own a Home in UAE
- Stakeholders in Housing System
Overview of the UAE Housing System
The housing system in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape characterized by a diverse range of options that cater to both citizens and expatriates. In the UAE, the demand for housing has been driven by a thriving economy, a growing population, and the nation’s increasing prominence on the global stage. The housing market offers various accommodations, including apartments, villas, and townhouses. Dubai and Abu Dhabi, the two largest cities, are known for their iconic skyscrapers and luxurious apartment complexes, while other emirates like Sharjah and Ras Al Khaimah provide a more traditional and family-friendly housing environment.
One of the distinctive features of the UAE’s housing system is the clear distinction between freehold and leasehold properties. Expatriates can own freehold properties in certain designated areas, while in other areas, they can lease properties for 99 years. These provisions have attracted real estate investments from around the world and have contributed significantly to the development of the housing sector.
Additionally, the UAE government has implemented various initiatives to address the issue of affordable housing, offering subsidies and grants to Emirati citizens. The establishment of mortgage institutions and regulations has also facilitated homeownership for both citizens and expatriates.
The real estate market in the UAE has faced fluctuations, particularly due to global economic conditions and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite these challenges, the UAE remains an attractive destination for property investments and offers many options that cater to diverse needs, from luxury high-rise apartments to family-friendly suburban communities.
Entities Involved in the UAE Housing System
The housing system in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is overseen and managed by several government entities and departments at the federal and emirate levels. Here are some key entities involved:
UAE Ministry of Infrastructure Development: This federal ministry plays a vital role in infrastructure and housing development, overseeing various housing projects and initiatives. This ministry plays a crucial role in ensuring that the UAE’s infrastructure aligns with the nation’s rapid economic growth and increasing urbanization. It oversees a wide range of projects related to transportation, housing, and utilities, contributing to the development of modern cities and sustainable communities. The Ministry of Infrastructure Development collaborates closely with other federal and emirate-level government entities to plan and execute large-scale infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, utilities, and housing developments, that are essential to the country’s progress.
Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA): RERA is responsible for regulating and supervising the real estate sector in Dubai, including monitoring real estate development, licenses, and escrow accounts. Established in 2007, RERA’s primary mandate is to ensure transparency, accountability, and professionalism within the real estate industry. It oversees various aspects of the sector, including the registration and regulation of real estate developers, brokers, and agents, as well as the monitoring of real estate projects, licensing of real estate service providers, and management of escrow accounts. RERA’s efforts have contributed to Dubai’s reputation as a trusted and attractive destination for real estate investments, both for local and international investors.
Abu Dhabi Housing Authority: The Abu Dhabi Housing Authority was established to address the housing needs of UAE citizens, the authority is dedicated to ensuring that residents have access to high-quality, affordable housing options. It works on various housing projects, including the development of residential communities and affordable housing units. The Abu Dhabi Housing Authority is committed to improving the living standards and quality of life for its citizens, aligning with the broader goals of the UAE government to provide sustainable and comfortable living conditions.
Dubai Land Department: Dubai Land Department was established to ensure transparency and efficiency in the real estate sector, this department plays a pivotal role in managing property registration, licensing real estate professionals, and implementing regulatory measures. It maintains a comprehensive and up-to-date database of property transactions and ownership, which adds to the transparency and reliability of the real estate market in Dubai. The Dubai Land Department’s efforts are pivotal in fostering trust and confidence among investors, both local and international, and in positioning Dubai as a prime destination for real estate investment.
Sharjah Real Estate Registration Department: The Sharjah Real Estate Registration Department was established to ensure transparency, security, and efficiency in the real estate sector, this department plays a vital role in maintaining and regulating property records and land titles. It facilitates property transfers, lease registrations, and other real estate-related services, contributing to the trust and stability of the real estate market in Sharjah. The department’s efforts have streamlined property transactions and added to the ease of doing business in the emirate, attracting both local and international investors.
Ras Al Khaimah Real Estate Regulatory Authority: Ras Al Khaimah Real Estate Regulatory Authority Established to promote transparency and professionalism within the real estate industry, this authority plays a pivotal role in managing real estate transactions, regulating real estate development, and licensing real estate professionals and firms. It ensures that all real estate activities adhere to specific standards and legal requirements, contributing to the credibility and reliability of the real estate market in Ras Al Khaimah. The authority’s initiatives have attracted investments from both local and international investors, establishing Ras Al Khaimah as an emerging and competitive destination for real estate opportunities.

Types of Houses in UAE
The UAE offers a diverse range of housing options to cater to the needs and preferences of its residents. These include high-rise apartments in cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi, favored by professionals and expatriates for their convenience. Villas and townhouses are popular in suburban areas, providing larger living spaces and private gardens, making them ideal for families. Luxurious penthouses offer spacious layouts and stunning views from the top floors of skyscrapers. Gated compounds and residential communities provide shared facilities and security, enhancing family-friendly living. Affordable housing initiatives target Emirati citizens, while serviced apartments and historical houses showcase the country’s rich heritage.
Some of the prominent types of houses in the UAE include:
Apartments: Apartments in the UAE are a prevalent and sought-after type of housing, especially in the bustling cities of Dubai and Abu Dhabi. These high-rise residential buildings offer a wide range of apartment sizes, from cozy studios to spacious penthouses, accommodating both single professionals and families. Apartments are favored for their modern amenities, convenient locations, and proximity to key business and leisure hubs. Many feature luxurious finishes, stunning city views, and a host of on-site facilities, including gyms, swimming pools, and 24-hour security.

Villas: Villas are a prevalent and cherished housing choice in the United Arab Emirates, particularly in suburban areas and gated communities. These spacious and often luxurious standalone homes offer residents a unique lifestyle with private gardens and greater living space, making them ideal for families. Villas come in various sizes and architectural styles, from contemporary designs to those reflecting traditional Emirati and Arabian aesthetics. These homes often include multiple bedrooms, spacious living areas, and outdoor spaces, creating a sense of privacy and tranquility. Villas are a popular choice for those seeking a more traditional, family-oriented, and expansive living environment, away from the hustle and bustle of city life, while still enjoying the modern amenities and services readily available in the UAE.

Penthouses: Penthouses in the United Arab Emirates represent the epitome of luxury living in the country. These exclusive homes are typically situated on the uppermost floors of high-rise residential buildings and offer a unique lifestyle characterized by opulence and panoramic views. Penthouses are known for their spacious layouts, high-end finishes, and premium amenities, such as private rooftop terraces, swimming pools, and sometimes even private elevators. These properties often feature floor-to-ceiling windows, flooding the living spaces with natural light and providing breathtaking views of the cityscape or waterfront.

Gated Communities: These communities consist of villas or townhouses located within a controlled and restricted-access environment. They are characterized by a range of shared amenities, including swimming pools, parks, sports facilities, and 24-hour security services, ensuring a safe and family-friendly living environment. Gated communities provide a sense of community and offer an ideal living solution for families and those who value privacy and exclusivity. These neighborhoods are often located in suburban areas, away from the bustling city centers, providing a tranquil atmosphere while still being conveniently accessible to urban amenities. The concept of gated communities aligns with the UAE’s commitment to offering diverse housing options that cater to a broad spectrum of preferences and lifestyles.

Historical Houses: Historical houses in the United Arab Emirates are more than just dwellings; they are living artifacts that reflect the rich heritage and culture of the country. Preserved to showcase traditional Emirati architecture, these houses provide a glimpse into the way of life of the past. They are characterized by elements like wind towers (barrel), courtyard designs, and mud-brick construction. Visitors and residents can explore the historical significance of these homes, often turned into museums or cultural centers, offering a fascinating journey into the country’s roots. Historical houses are essential in preserving and celebrating the UAE’s cultural identity, making them important landmarks and educational hubs where the past is honored and shared with the present and future generations.

Floating Homes: Floating homes represent a unique and innovative type of housing in the United Arab Emirates, particularly in dynamic cities like Dubai. These homes are situated on the water, offering a lifestyle that combines luxury living with waterfront tranquility. Floating homes are characterized by their contemporary designs and state-of-the-art features, including modern interiors, spacious living areas, and expansive decks that provide stunning views of the surrounding waterways. These properties often come with facilities like private docks, ensuring easy access to the sea or nearby attractions. Floating homes offer a distinctive living experience that appeals to those who appreciate the charm of waterfront living while enjoying the comforts and conveniences of urban life.

Affordable Housing: Affordable housing is an integral part of the United Arab Emirates’ commitment to providing its citizens with comfortable and accessible living options. The UAE government has initiated various programs and incentives to ensure that affordable housing is available to Emirati citizens. These housing options are characterized by lower prices, subsidized interest rates on mortgages, and favorable financing terms. They are designed to help Emirati nationals achieve their homeownership goals, supporting the vision of sustainable and stable communities. Affordable housing initiatives include the construction of residential units and communities that are well-equipped with essential amenities and services.

Serviced Apartments: Serviced apartments in the United Arab Emirates offer a flexible and convenient housing solution that caters to both short-term and long-term residents. These fully furnished and equipped apartments come with a range of amenities and services typically found in hotels, such as housekeeping, concierge, and room service. Serviced apartments are particularly popular among expatriates, business travelers, and tourists who seek a comfortable and hassle-free living experience. These apartments provide a home away from home, allowing residents to enjoy the benefits of a private living space while also having access to hotel-like services. Serviced apartments in the UAE are available in various sizes, from studios to multi-bedroom units, and they are often strategically located in prime areas of cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi, ensuring convenient access to business districts, shopping centers, and entertainment hubs.

Ways to Own a Home in UAE
Owning a home in the United Arab Emirates offers various pathways to accommodate different needs and financial situations. For UAE nationals and certain expatriates, direct purchase of freehold property is common, providing full ownership rights. Long-term leases, often lasting 99 years, are available in areas where full ownership by expatriates is restricted. Mortgages from local and international banks facilitate property purchases by spreading costs over time. Off-plan properties allow buyers to invest in developments before they are completed.
Joint ventures and shared ownership programs are additional options offered by some developers. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) enable investors to participate in real estate portfolios without direct property ownership. Government initiatives provide support for Emirati citizens’ homeownership goals, demonstrating the UAE’s commitment to making housing accessible to its residents and expatriate population.
In the United Arab Emirates, there are several ways to own a home, catering to the diverse needs and preferences of residents and investors. These include:
Freehold Ownership: Freehold ownership is a significant and sought-after way to own a home in the United Arab Emirates, primarily available to UAE nationals and certain categories of expatriates. It grants the buyer full ownership rights over the property, including both the structure and the land it’s built on. This means that the owner has complete control over the property, with the freedom to sell, rent, or pass it on to heirs. Some of the most prestigious and high-demand properties in the UAE, especially in cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi, fall under the category of freehold, making them desirable investments for both Emiratis and expatriates looking for a permanent stake in the country. The accessibility of freehold ownership in the UAE underscores the nation’s openness to foreign investment and its commitment to providing a welcoming and investor-friendly environment in the real estate sector.
Long-Term Leasehold: Long-term leasehold is a popular and pragmatic method for owning a home in the United Arab Emirates, particularly for non-UAE nationals in areas where freehold ownership is restricted. Under this arrangement, individuals can enter into long-term lease agreements, often lasting for 99 years, granting them exclusive rights to the property for the duration of the lease. This offers a high degree of security and the practical benefits of homeownership without full ownership rights. Residents can enjoy the comforts and privacy of their homes and make long-term investments while adhering to local regulations. Long-term leasehold reflects the UAE’s commitment to making property ownership accessible and secure for both its citizens and expatriate population, catering to a diverse range of housing preferences and financial capacities.
Mortgages: Mortgages are a common and accessible means of owning a home in the United Arab Emirates, offered by local and international banks. With the UAE’s vibrant real estate market, mortgages provide a flexible way for residents, both Emirati citizens and expatriates, to finance their property purchases. Mortgages typically come with competitive interest rates and flexible terms, making them an attractive option for those looking to spread the cost of homeownership over an extended period. Buyers can choose from various financing options, including fixed and variable rates, and the mortgage application process is straightforward and efficient.
Off-Plan Properties: Off-plan properties are those that are purchased before they are completed or even before construction begins. This approach is favored for several reasons. First, it often comes with a more affordable price tag compared to ready properties, making it an attractive option for investors. Second, off-plan buyers have the opportunity to customize the property and choose from various unit types and layouts. Finally, the potential for significant appreciation in property value by the time of completion can yield substantial returns on investment. Off-plan properties are abundant in the UAE’s dynamic real estate market, particularly in cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi, making them a sought-after choice for investors and those looking for their future homes.
Joint Ventures: Joint ventures offer a distinctive and cooperative approach to owning a home in the United Arab Emirates. In this model, buyers enter into partnerships with developers to collectively own and operate a property or development. Joint ventures are typically structured as co-ownership arrangements where investors share in the property’s revenues, rental income, or future proceeds. This unique approach allows for a diverse range of ownership options and can be particularly appealing to those who want to invest in real estate without the full responsibilities of sole ownership. It can also mitigate financial risks while fostering a collaborative and shared approach to property investment. Joint ventures are facilitated by developers in the UAE, and the terms and structures can vary, offering an innovative and inclusive way to participate in the country’s vibrant real estate market.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) provide a different avenue for owning a stake in real estate in the United Arab Emirates. In this investment model, individuals can become part-owners of real estate assets and portfolios without direct property ownership. Instead, they invest in publicly traded or private REITs, which manage and own a diversified range of income-generating real estate properties such as residential and commercial buildings, hotels, and shopping centers. REITs offer an attractive option for those seeking exposure to the real estate market without the responsibilities of property management. They provide a liquid and accessible investment platform, enabling investors to diversify their portfolios and benefit from rental income and capital appreciation. REITs are regulated by the UAE’s Securities and Commodities Authority, offering a transparent and well-governed way to participate in the country’s thriving real estate sector.
Government Initiatives: Government initiatives play a pivotal role in facilitating homeownership in the United Arab Emirates. The UAE government has implemented various programs and schemes to make property ownership more accessible and affordable, primarily for its citizens. These initiatives often include grants, subsidies, and favorable financing terms. For example, the Sheikh Zayed Housing Program provides financial assistance to UAE nationals to purchase or build their homes. Additionally, the Mohammed bin Rashid Housing Establishment offers housing solutions and support to UAE citizens.
These programs reflect the government’s commitment to ensuring that Emirati citizens can achieve their homeownership goals. Furthermore, initiatives such as the “50-Year Golden Visa” and long-term visas for retirees contribute to the overall attractiveness of owning property in the UAE for both citizens and expatriates. The UAE’s government initiatives align with the country’s vision of promoting stable and thriving communities and offering diverse housing solutions to its residents.
Stakeholders in Housing System
The housing system in the United Arab Emirates involves several key stakeholders, including government entities, real estate developers, financial institutions, and property investors. Government entities, such as the UAE Ministry of Infrastructure Development and the UAE Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA), play a regulatory and supervisory role, ensuring that housing policies and regulations are effectively implemented.
Real estate developers are instrumental in building and delivering residential properties, responding to the diverse housing needs of the population. Financial institutions, including local and international banks, facilitate property ownership through mortgage financing. Property investors, both local and international, contribute to the vibrancy of the real estate market and play a role in shaping the property landscape. The collaboration and interaction of these stakeholders ensure that the UAE’s housing system remains dynamic, responsive, and accommodating to the diverse requirements of its residents and investors.
Government Entities: Government bodies such as the UAE Ministry of Infrastructure Development, the UAE Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA), and local municipalities are responsible for setting the rules that shape the property market. These regulations cover various aspects, including property ownership, construction standards, land use, and rental laws. Government entities also oversee the implementation of these policies, ensuring that the housing market remains well-regulated and transparent.
Real Estate Developers: Private and public sector developers are responsible for building, developing, and managing residential properties. They create a diverse range of housing options to meet the needs and demands of residents and investors. These developers are responsible for creating a wide range of housing options, including apartments, villas, townhouses, and luxury estates. They work to meet the demands of various segments of the market, from affordable housing solutions to high-end, luxury properties. Real estate developers are instrumental in shaping the physical landscape of the UAE, with iconic structures and master-planned communities that have transformed the country’s cities. Their projects contribute to the growth of the real estate sector, attracting both local and international investors and residents.
Financial Institutions: Local and international banks, as well as other financial organizations, play a crucial role in facilitating property ownership. They offer a range of financial services, including mortgage financing, which enables individuals and families to purchase homes by spreading the cost over an extended period. These institutions provide competitive interest rates, flexible terms, and various mortgage options, making homeownership more accessible to both Emirati citizens and expatriates. Through mortgage lending, financial institutions stimulate demand in the real estate market, boosting property transactions and supporting the growth of the housing sector.
Property Investors: Property investors often seek opportunities to generate income, diversify their investment portfolios, and benefit from potential property appreciation. Their investments influence property prices, trends, and overall market conditions. Additionally, property investors contribute to the growth and development of the UAE’s real estate sector, fostering a thriving environment for property transactions and construction activities. Their engagement underscores the attractiveness of the UAE’s property market, known for its stability, strategic location, and promising returns on investment, making it a preferred destination for real estate investors from around the world.
Real Estate Brokers and Agents: Real estate professionals assist buyers, sellers, and tenants in navigating the property market, helping them find suitable housing solutions. They serve as intermediaries between property buyers and sellers, helping individuals and families navigate the complex real estate market. These professionals possess in-depth knowledge of the property landscape, local regulations, and market trends, which they use to assist clients in making informed decisions. Real estate brokers and agents help buyers find the right property that matches their needs and budget, and they assist sellers in marketing their properties effectively. Their expertise streamlines property transactions and contributes to the overall transparency and efficiency of the housing market.
Property Management Companies: These companies are responsible for the management and maintenance of residential properties, ensuring that they remain in good condition and providing a quality living environment for residents. They specialize in the professional management and maintenance of residential properties, ensuring that these properties remain in optimal condition and providing a high-quality living environment for residents. Property management companies oversee a wide range of responsibilities, including rent collection, property maintenance, security, and tenant relations.
Residents: Individuals and families are crucial stakeholders in the housing system, as they make choices regarding property purchase, rental, and use, shaping the demand for various housing options. They include both Emirati citizens and expatriates who choose to live and work in the UAE. As stakeholders, residents drive the demand for various types of housing, shaping the real estate market’s dynamics. They make choices regarding property purchase, rental, or lease agreements, directly influencing the occupancy rates and property values. Additionally, residents have a vested interest in housing policies, tenant rights, and property regulations that impact their living conditions and investment decisions. The UAE government is dedicated to providing diverse and affordable housing solutions to cater to the needs of its resident population, underscoring the importance of residents’ roles in the housing system.
